Abstract
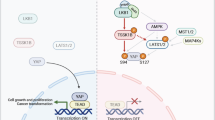
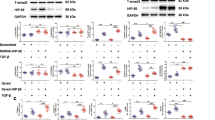
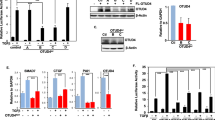
Members of the TGF-β family of growth factors signal from the cell surface through serine/threonine kinase receptors. Intracellular propagation of the signal occurs by phosphorylation of intracellular proteins of the Smad family. Smad7 belongs to the subclass of inhibitory Smads that function as antagonists of TGF-β signaling. A yeast two-hybrid screen of a human placental cDNA expression library using full-length mouse Smad7 as bait identified Yes-Associated Protein (YAP65) as a novel Smad7-interacting protein. The association of Smad7 with YAP65 was confirmed using co-expressed tagged proteins in COS-7 cells. Deletion of the PY motif of Smad7 reduced but did not abolish YAP65-Smad7 association, suggesting the existence of several interacting domains. We demonstrate that YAP65 potentiates the inhibitory activity of Smad7 against TGF-β-induced, Smad3/4-dependent, gene transactivation. Furthermore, YAP65 augments the association of Smad7 to activated TGF-β receptor type I (TβRI), whereas YAP65(1–301), which exerts a dominant-negative effect against Smad7-driven inhibition of TGF-β signaling, reduces these interactions. Together, these data provide the first evidence that YAP65 is a Smad7 partner that facilitates the recruitment of the latter to activated TβRI, and enhances the inhibitory activity of Smad7 against TGF-β signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attisano L, Wrana JL . 2000 Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12: 235–243
Branton MH, Kopp JB . 1999 Microbes Infect. 1: 1349–1365
Datta PK, Chytil A, Gorska AE, Moses HL . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 34671–34674
Datta PK, Moses HL . 2000 Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 3157–3167
de Caestecker MP, Piek E, Roberts AB . 2000 J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 92: 1388–1402
Dennler S, Itoh S, Vivien D, ten Dijke P, Huet S, Gauthier JM . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 3091–3100
Ebisawa T, Fukuchi M, Murakami G, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Imamura T, Miyazono K . 2001 J. Biol. Chem. 276: 12477–12480
Kavsak P, Rasmussen RK, Causing CG, Bonni S, Zhu H, Thomsen GH, Wrana JL . 2000 Mol. Cell. 6: 1365–1375
Lallemand F, Mazars A, Prunier C, Bertrand F, Kornprost M, Gallea S, Roman-Roman S, Cherqui G, Atfi A . 2001 Oncogene 20: 879–884
Landstrom M, Heldin NE, Bu S, Hermansson A, Itoh S, ten Dijke P, Heldin CH . 2000 Curr. Biol. 10: 535–538
Massagué J, Wotton D . 2000 EMBO J. 19: 1745–1754
Mazars A, Lallemand F, Prunier C, Marais J, Ferrand N, Pessah M, Cherqui G, Atfi A . 2001 J. Biol. Chem. 276: 36797–36803
Musacchio A, Wilmanns M, Saraste M . 1994 Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 61: 283–297
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Moren A, Nakayama T, Christian JL, Heuchel R, Itoh S, Kawabata M, Heldin NE, Heldin CH, ten Dijke P . 1997 Nature 389: 631–635
Rotin D . 1998 Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 228: 115–133
Songyang Z, Fanning AS, Fu C, Xu J, Marfatia SM, Chishti AH, Crompton A, Chan AC, Anderson JM, Cantley LC . 1997 Science 275: 73–77
Sudol M . 1994 Oncogene 9: 2145–2152
Sudol M, Sliwa K, Russo T . 2001 FEBS Lett. 490: 190–195
Topper JN, Cai J, Qiu Y, Anderson KR, Xu YY, Deeds JD, Feeley R, Gimeno CJ, Woolf EA, Tayber O, Mays GG, Sampson BA, Schoen FJ, Gimbrone Jr MA, Falb D . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 9314–9319
Vojtek AB, Hollenberg SM, Cooper JA . 1993 Cell 74: 205–214
Wieser R, Wrana JL, Massagué J . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 2199–2208
Wrana JL . 2000 Cell 100: 189–192
Yagi R, Chen LF, Shigesada K, Murakami Y, Ito Y . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 2551–2562
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Drs S Dennler, J-M Gauthier, Y Ito, K Miyazono, JN Topper and JL Wrana, who provided us with expression plasmids essential for this study. Supported by INSERM, CNRS, Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC), Fondation de France, and Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (LNCC), France. O Ferrigno and F Lallemand are recipients of ARC and Fondation de France post-doctoral fellowships, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrigno, O., Lallemand, F., Verrecchia, F. et al. Yes-associated protein (YAP65) interacts with Smad7 and potentiates its inhibitory activity against TGF-β/Smad signaling. Oncogene 21, 4879–4884 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205623
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205623
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A low amino acid environment promotes cell macropinocytosis through the YY1-FGD6 axis in Ras-mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Oncogene (2022)
-
Mechanical control of nuclear import by Importin-7 is regulated by its dominant cargo YAP
Nature Communications (2022)
-
The essential role of TAZ in normal tissue homeostasis
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2021)
-
Targeting the YAP-TEAD interaction interface for therapeutic intervention in glioblastoma
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2021)
-
Gone Caving: Roles of the Transcriptional Regulators YAP and TAZ in Skeletal Development
Current Osteoporosis Reports (2020)