Abstract
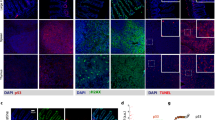
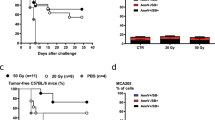
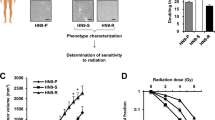
We have analysed the radiation response of a human medullary thyroid carcinoma cell line (MTT), characterized by the absence of a functional p53 protein, and the consequences of MDM2 overexpression in this process. We show that the product of the mdm2 proto-oncogene is able to sensitize MTT cells to ionizing radiation. After radiation treatment, MTT cells display histograms consistent with a G2M arrest. MTT cells expressing MDM2 (MTT-mdm2) are unable to respond to DNA damage with G2M arrest, and display a high percentage of apoptosis. MTT-mdm2 cells show high levels of E2F-1 protein, suggesting that the induction of apoptosis observed upon MDM2 overexpression could be dependent on E2F-1. This observation is further supported with assays showing that E2F-1 binding to specific DNA sequences is enhanced in MTT-mdm2 cells. Likewise, transactivation of reporter constructs exclusively dependent on E2F-1 is also elevated after transfection with MDM2. This effect can be reverted by transient transfection with p19ARF. To link the expression of E2F-1 with the induction of apoptosis, we generated clonal cell lines overexpressing E2F-1. Transfection with E2F-1 results in a low number of outgrowing colonies with reduced proliferation rates, indicating that E2F-1 is deleterious for cell growth. This negative regulation correlates with an increase in the percentage of the cell population with DNA content below 2N, suggesting that E2F-1 promotes apoptosis. Finally, overexpression of E2F-1 sensitizes MTT cells to radiation exposure. We conclude that the effects observed by MDM2 overexpression could be mediated by E2F-1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright N . 1987 Radiat. Res. 112: 331–340
Alkhalaf M, Ganguli G, Messaddeq N, Le Meur M, Wasylyk B . 1999 Oncogene 18: 1419–1434
Andrews NC, Faller DV . 1991 Nucleic Acid Res. 19: 2499–
Banerjee D, Schnieders B, Fu JZ, Adhikari D, Zhao SC, Bertino JR . 1998 Cancer Res. 58: 4292–4296
Blattner C, Sparks A, Lane D . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 3704–3713
Brown DR, Thomas CA, Deb SP . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 2513–2525
Cachilly-Snyder L, Yang-Feng T, Francke U, George DL . 1987 Somatic Cell. Mol. Genet. 13: 235–244
Carlomagno F, Salvatore D, Santoro M, de Franciscis V, Quadro L, Panariello L, Colantuoni V, Fusco A . 1995 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 207: 1022–1028
Chang EH, Pirollo KF, Zou ZQ, Cheung HY, Lawler EL, Garner R, White E, Bernstein WB, Fraumeni JW, Blattner WA . 1987 Science 237: 1036–1038
Chen CY, Oliner JD, Zhan Q, Fornace AJ, Vogelstein B, Kastan MB . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 2684–2688
Dilla T, Velasco JA, Medina DL, Gonzalez-Palacios JF, Santisteban P . 2000 Endocrinology 141: 420–429
Dong YB, Yang HL, Jane M, Liu TJ, Stilwell A, Atienza C, McMasters KM . 1999 Cancer 86: 2021–2033
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . 1993 Cell 75: 817–825
Finlay CA . 1993 Mol. Cell. Biol. 13: 301–306
Ganguli G, Abecassis J, Wasylyk B . 2000 EMBO J. 19: 5135–5147
Giuffrida D, Gharib H . 1998 Ann. Oncol. 9: 695–701
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M . 1997 Nature 387: 296–299
Helin K, Lees JA, Vidal M, Dyson N, Harlow E, Fattaey A . 1992 Cell 24: 337–350
Heshmati HM, Gharib H, Van Heerden JA, Sizemore GW . 1997 Am. J. Med. 103: 60–69
Hunt KK, Deng J, Liu TJ, Wilson-Heiner M, Swisher SG, Clayman G, Hung MC . 1997 Cancer Res. 57: 4722–4726
Hwang A, Muschel RJ . 1998 Radiat. Res. 150: S52–S59
Illiakis G . 1997 Seminars Oncol. 24: 602–615
Johnson DG . 2000 Mol. Carcinog. 27: 151–157
Kasid U, Pfeiffer A, Brennan T, Beckett M, Weichselbaum RR, Dritschilo A, Mark GE . 1989 Science 243: 1354–1356
Kelle DE, Zyndi F, Ashmun RA, Sherr JC . 1995 Cell 83: 993–1000
Kubbutat MHG, Jones SN, Vousden KH . 1997 Nature 387: 299–303
Lam EW, Watson RJ . 1993 EMBO J. 12: 2705–2713
Leong SS, Horoszewicz JS, Shimaoka K, Friedman M, Kawinski E, Song MJ, Zeigel R, Chu TM, Bayling SB, Mirand EA . 1981 Advances in thyroid neoplasia Andreoli M, Monaco F, Robbins J (eds) Rome, Field Educational Italia pp 95–108
Lin WC, Lin FT, Nevins JR . 2001 Genes Dev. 15: 1833–1844
Liu TJ, Wang M, Breau LR, Henderson Y, El Naggar AK, Steck KD, Siccard MW, Clayman GL . 1999 Cancer Gene Ther. 6: 163–171
Loughran O, La Thange NB . 2000 Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 2186–2197
Lozano G, Montes de Oca Luna R . 1998 Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1377: M55–M59
Martin K, Trouche D, Hagemeler C, Sorensen TS, La Thange NB, Kouzarides T . 1995 Nature 375: 691–694
Medina DL, Velasco JA, Santisteban P . 1999 Endocrinology 140: 87–95
Momand J, Zambetti GP . 1997 J. Cell. Biochem. 64: 343–352
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ . 1992 Cell 69: 1237–1245
Nelkin BD, De Bustos A, Mabry M, Baylin SB . 1989 J. Amer. Med. Ass. 261: 3130–3135
Ohtani K . 1999 Front. Biosci. 4: D793–D804
Oliner JD, Kinzler KW, Meltzer PS, George DL, Vogelstein B . 1992 Nature 358: 80–83
Oswald F, Lovec H, Moroy T, Lipp M . 1994 Oncogene 9: 2029–2036
Phillips AC, Ernst MK, Bates S, Rice NR, Vousden KH . 1999 Mol. Cell 4: 771–781
Pirollo KF, Tong YA, Villegas Z, Chen Y, Chang EH . 1993 Radiat. Res. 135: 234–243
Puxeddu E, Fagin JA . 2001 Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 30: 493–513
Pruschy M, Wirbelauer C, Glanzmann C, Bodis S, Krek W . 1999 Cell Growth Differ. 10: 141–146
Sawey MJ, Hoot TA, Burns FJ, Garte SJ . 1987 Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 932–935
Varghese S, Jung M . 1998 Arch. Pharma. Res. 21: 640–644
Vecchio G, Santoro M . 2000 Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 38: 113–116
Velasco JA, Acebron A, Zannini M, Martin-Perez J, Di Lauro R, Santisteban P . 1998 Endocrinology 139: 2796–2802
Velasco JA, Medina DL, Romero J, Mato ME, Santisteban P . 1997 Int. J. Cancer 73: 449–455
Zhan Q, Fan S, Bae I, Guillouf C, Liebermann DA, O'Connor PM, Fornace Jr AJ . 1994 Oncogene 9: 3743–3751
Zhang R, Wang H . 2000 Current Pharmac. Design 6: 393–416
Zhang Y, Xiong Y, Yarbrough G . 1998 Cell 92: 725–734
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Vicente Notario from Georgetown University Medical Center for critical reading of the manuscript. Tatiana Dilla is recipient of a fellow from the Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias. The work is supported by grants from the Comunidad de Madrid (CAM 08.1/0025/1997), Dirección General de Ciencia y Tecnología (BMC-2001-2087) and Fundación Salud 2000 (Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dilla, T., Romero, J., Sanstisteban, P. et al. The mdm2 proto-oncogene sensitizes human medullary thyroid carcinoma cells to ionizing radiation. Oncogene 21, 2376–2386 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205307
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205307
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The therapy and mechanisms of replication-deficient recombinant adenovirus Ad-p14ARF in hepatocellular carcinoma
The Chinese-German Journal of Clinical Oncology (2007)