Abstract
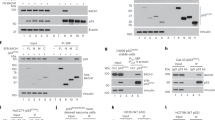
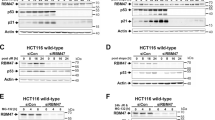
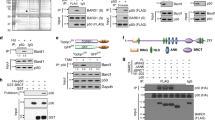
Bloom syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder associated with mutations in BLM gene encoding protein that belongs to the family of DNA helicases. It is characterized by predisposition to cancer, immunodeficiency, high sensitivity to UV and genomic instability of somatic cells. Here we show physical and functional cooperation between BLM and p53 proteins. Ectopic expression of BLM causes anti-proliferative effect in p53 wild type, but not in p53-deficient cells; p53-mediated transactivation is attenuated in primary fibroblasts from Bloom syndrome patients. BLM and p53 proteins physically interact in the cells as demonstrated in yeast and mammalian two-hybrid systems; interaction sites are mapped to 237–272 aa residues of BML and 285–340 aa of p53. Ectopic expression of the fragment of wild type BML containing p53-interactive domain suppresses p53-mediated transcription and interferes with p53-mediated growth inhibition. These observations indicate that BLM might be an important component of p53 function and suggest that Bloom Syndrome phenotype may in part be the result of the deregulation of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akashi M, Koeffler HP . 1998 Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 41: 172–199
El Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . 1993 Cell 75: 817–825
Ellis NA, Groden J, Ye TZ, Straughen J, Lennon DJ, Ciocci S, Proytcheva M, German J . 1995 Cell 83: 655–666
Ellis NA, Roe AM, Kozloski J, Proytcheva M, Falk C, German J . 1994 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 55: 453–460
Garkavtsev IV, Grigorian IA, Chernov MV, Ossovskaya VS, Chumakov PM, Gudkov AV . 1998 Nature 391: 295–298
German J . 1993 Medicine (Baltimore) 72: 393–406
Komarova EA, Chernov MV, Franks R, Wang K, Armin G, Zelnick CR, Chin DM, Bacus SS, Start GR, Gudkov AV . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 1391–1400
Lu X, Lane DP . 1993 Cell 75: 765–778
Mohaghegh P, Karow JK, Brosh Jr RM, Bohr VA, Hickson ID . 2001 Nucleic Acids Res. 29: 2843–2849
Morozov V, Mushegian AR, Koonin EV, Bork P . 1997 Trends Biochem. Sci. 22: 417–418
Morgenstern JP, Land H . 1990 Nucleic Acids Res. 18: 3587–3596
Ossovskaya VS, Mazo IA, Chernov MV, Chernova OB, Strezoska Z, Kondratov R, Stark GR, Chumakov PM, Gudkov AV . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 10309–10314
Prives C, Hall PA . 1999 J. Pathol. 187: 112–126
Spillare EA, Robles AI, Wang XW, Shen JC, Yu CE, Schellenberg GD, Harris CC . 1999 Genes Dev. 13: 1355–1360
Wallace-Brodeur RR, Lowe SW . 1999 Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 55: 64–75
Wang XW, Tseng A, Ellis NA, Spillare EA, Linke SP, Robles AI, Seker H, Yang Q, Hu P, Beresten S, Bemmels NA, Garfield S, Harris CC . 2001 J. Biol. Chem. 276: 32948–32955
Acknowledgements
We thank NA Ellis for providing full-length BLM cDNA. This work was supported by NIH grant CA75179 to AV Gudkov.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garkavtsev, I., Kley, N., Grigorian, I. et al. The Bloom syndrome protein interacts and cooperates with p53 in regulation of transcription and cell growth control. Oncogene 20, 8276–8280 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205120
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RecQ helicases; at the crossroad of genome replication, repair, and recombination
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)
-
p53: traffic cop at the crossroads of DNA repair and recombination
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2005)
-
RecQ family helicases: roles as tumor suppressor proteins
Oncogene (2002)