Abstract
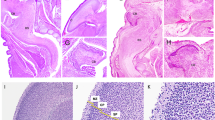
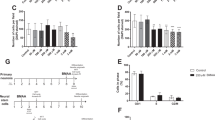
Neural precursor cells (NPCs) populate the embryonic ventricular zone and persist in the subependymal zone of the adult brain. We hypothesized that hereditary and/or acquired mutations in apoptosis-associated genes, such as p53 and caspases, may protect NPCs from DNA damage-induced death and predispose them to subsequent neoplastic transformation. To test this hypothesis, we exposed NPCs from wild-type and targeted gene-disrupted mouse embryos (p53, caspase-9, caspase-3, and bax mutants) to ethyl-nitrosourea (ENU), a known DNA mutagen and neural carcinogen, and measured NPC viability. We found that ENU produced caspase-3 activation and apoptotic NPC death 6–24 h after administration both in vivo and in vitro. This effect was critically dependent on p53 and caspase-9 expression. The long-term effect of intrauterine ENU exposure was examined in control and p53-deficient mice. High grade glial tumors were found in 60% of p53−/− young adult mice exposed to ENU on gestational day 12.5 but not in p53+/− or p53+/+ littermates or in untreated p53-deficient mice. All the tumors were located supratentorially and possessed strong immunoreactivity for glial fibrillary acidic protein and the anti-apoptotic molecule Bcl-XL. These results suggest that intrauterine exposure of NPCs to certain DNA damaging agents may synergistically interact with specific genetic abnormalities (e.g. p53 deficiency) to produce glial neoplasms in the adult brain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloyz RS, Bamji SX, Pozniak CD, Toma JG, Atwal J . 1998 J. Cell Biol. 143: 1691–1703
Armstrong RC, Aja TJ, Hoang KD, Gaur S, Bai X, Alnemri ES, Litwack G, Karanewsky DS, Fritz LC, Tomaselli KJ . 1997 J. Neurosci. 17: 553–562
Bilzer T, Reifenberger G, Wechsler W . 1989 Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 11: 551–556
Bruggers CS, Fults D, Perkins SL, Coffin CM, Carroll WL . 1999 J. Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. 21: 19–25
D'Sa-Eipper C, Leonard JR, Putcha G, Zheng TS, Flavell RA, Rakic P, Kuida K, Roth KA . 2001 Development 128: 137–146
D'Sa-Eipper C, Roth KA . 2000 Devel. Neurosci. 22: 116–124
Diwan BA, Meier H . 1974 Cancer Res. 34: 764–770
Doetsch F, Caillé I, Lim DA, García-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylia A . 1999 Cell 97: 703–716
Dole M, Nuñez G, Merchant AK, Maybaum J, Rode CK, Block CA, Castle VP . 1994 Cancer Res. 54: 3253–3259
Dole MG, Jasty R, Cooper MJ, Thompson CB, Nuñez G, Castle VP . 1995 Cancer Res. 55: 2576–2582
Druckrey H, Ivankovic S, Preussmann R . 1966 Nature 210: 1378–1379
Eves EM, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Wagner AJ, Hay N, Rosner MR . 1996 J. Neurochem. 67: 1908–1920
Frank KM, Sekiguchi JM, Seidl KJ, Swat W, Rathbun GA, Cheng H-L, Davidson L, Kangaloo L, Alt FW . 1998 Nature 396: 173–177
Haydar TF, Wang F, Schwartz ML, Rakic P . 2000 J. Neurosci. 20: 5764–5774
Jacks T, Remington L, Williams BO, Schmitt EM, Halachmi S, Bronson RT, Weinberg RA . 1994 Curr. Biol. 4: 1–7
Johansson CB, Momma S, Clarke DL, Risling M, Lendahl U, Frisén J . 1999 Cell 96: 25–34
Johnson MD, Kinoshita Y, Xiang H, Ghatan S, Morrison RS . 1999 J. Neurosci. 19: 2996–3006
Johnson MD, Xiang H, London S, Kinoshita Y, Knudson M, Mayberg M, Korsmeyer SJ, Morrison RS . 1998 J. Neurosci. Res. 54: 721–733
Kleihues P, Burger PC, Collins VP, Newcomb EW, Ohgaki H, Cavenee WK . 2000 World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. Kheihues P and Cavenee WK (ed) IARC Press: Lyon pp. 29–39
Klein MA, Rüedi D, Nozaki M, Dell EW, Diserens A-C, Seelentag W, Janzer RC, Aguzzi A, Hegi ME . 2000 Oncogene 19: 5329–5337
Krajewski S, Krajewski M, Ehrmann J, Sikorska M, Lach B, Chatten J, Reed JC . 1997 Am. J. Path. 150: 805–814
Liu R, Page C, Beidler DR, Wicha MS, Núñez G . 1999 Am. J. Pathol. 155: 1861–1867
McKay R . 1997 Science 276: 66–71
Motoyama N, Wang F, Roth KA, Sawa H, Nakayama K-I, Nakayama K, Negishi I, Senju S, Zhang Q, Fujii S, Loh DY . 1995 Science 267: 1506–1510
Oda H, Zhang S, Tsurutani N, Shimizu S, Nakatsuru Y, Aizawa S, Ishikawa T . 1997 Cancer Res. 57: 646–650
Oppenheim RW, Flavell RA, Vinsant S, Prevette D, Kuan C-Y, Rakic P . 2001 J. Neurosci. 21: 4752–4760
Rao MS . 1999 The Anatomical Record 257: 137–148
Roth KA, Kuan C-Y, Haydar TF, D'Sa-Eipper C, Shindler KS, Zheng TS, Kuida K, Flavell RA, Rakic P . 2000 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 466–471
Schlegel J, Stumm G, Mennel HD . 1993 Exp. Toxic Pathol. 45: 455–466
Shindler KS, Latham CB, Roth KA . 1997 J. Neurosci. 17: 3112–3119
Srinivasan A, Roth KA, Sayers RO, Shindler KS, Wong AM, Fritz LC, Tomaselli KJ . 1998 Cell Death Diff. 5: 1004–1016
Stiles CD . 1998 Biochimica. et Biophysica. Acta. 1377: R1–R10
Timme T, Thompson TC . 1994 BioTechniques 17: 461–463
Watanabe K, Sato K, Biernat W, Tachibana O, von Ammon K, Ogata N, Yonekawa Y, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H . 1997 Clin. Cancer Res. 3: 523–530
Wechsler W, Kleihues P, Matsumoto S, Zülch KJ, Ivankovic S, Preussmann R, Druckrey H . 1969 Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 159: 360–408
Wechsler W, Rice JM, Vasselinovitch SD . 1979 Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 51: 219–226
Zaidi AU, D'Sa-Eipper C, Brenner J, Kuida K, Zheng TS, Flavell RA, Rakic P, Roth KA . 2001 J. Neurosci. 21: 169–175
Zheng TS, Schlosser SF, Dao T, Hingorani R, Crispe IN, Boyer JL, Flavell RA . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 13618–13623
Acknowledgements
We thank C Latham and J McDonough for expert technical assistance; and A Schmeckebier for secretarial support. Caspase-3 and caspase-9 mutant mice were generously provided by Dr RA Flavell (Yale University). CM1 antiserum was provided by Dr A Srinivasan (IDUN Pharmaceuticals, Inc.). This work was supported by postdoctoral training grant DK07296 to C D'Sa and grants from the Public Health Service to KA Roth.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leonard, J., D'Sa, C., Klocke, B. et al. Neural precursor cell apoptosis and glial tumorigenesis following transplacental ethyl-nitrosourea exposure. Oncogene 20, 8281–8286 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205024
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205024