Abstract
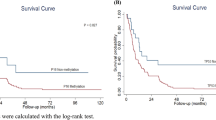
Death associated protein (DAP)-kinase is a 16 kDa calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine kinase that carries a death domain at its C-terminus. DAP-kinase functions as a positive mediator of apoptosis that is induced by interferon-γ. Recent studies suggest that DAP-kinase is involved in tumor metastasis and that it can be inactivated by methylation of CpG islands in the promoter region of the gene in some human tumors. However, little is known about the factors that are associated with the occurrence of DAP-kinase promoter methylation. We investigated both the possible associations of tobacco carcinogen and asbestos exposure with DAP-kinase promoter methylation, and the demographic and clinical factors associated with DAP-kinase promoter methylation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). One hundred and eighty-five patients diagnosed with NSCLC undergoing surgical resection from June, 1992 through December, 1996 at Massachusetts General Hospital participated in this study. Methylation-Specific PCR (MSP), performed using fresh-frozen tissue, was used to determine the methylation status of the promoter region of the DAP-kinase gene. Forty-seven (25%) of 185 tumors showed DAP-kinase promoter methylation. There was a significant association between methylation and an advanced pathologic stage (P=0.003, Fisher's exact test). Methylation of the DAP-kinase promoter was also associated with an increase in tumor size (P=0.009, Fisher's exact test) and lymph node involvement (P=0.04). No association was found between promoter methylation of DAP-kinase and k-ras or p53 mutation. In addition there was no association with a history of exposure to tobacco or asbestos. Controlling for age, sex, and histology, the odds ratios describing the association of DAP-kinase hypermethylation with stage were 2.70 (1.13–6.45), 3.11 (1.37–7.08) and 7.77 (1.21–50.03) in stages II, III and IV, respectively. Stage I cases with DAP-kinase promoter methylation had worse overall survival, but with the small sample size and limited follow-up this did not reach statistical significance. Our findings suggest that methylation of the promoter region of the DAP-kinase gene is not associated with exposure to tobacco or asbestos. However, they strongly suggest that DAP-kinase may be important in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer from early to late stage disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belinsky SA, Nikula KJ, Baylin SB, Issa JPJ . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 4045–4050
Bird AP . 1986 Nature 321: 209–213
Boyes J, Bird A . 1992 EMBO J. 11: 327–333
Brandeis M, Ariel M, Cedar H . 1993 BioEssays 15: 709–713
Cohen O, Feinstein E, Kimchi A . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 998–1008
Debbas M, White E . 1993 Genes Dev. 7: 546–554
Deiss LP, Feinstein E, Berissi H, Cohen O, Kimchi A . 1995 Genes Dev. 9: 15–30
Eguchi K, Kanai Y, Kobayashi K, Hirohashi S . 1997 Cancer Res. 57: 4913–4915
El-Deiry WA, Nelkin BD, Celano P, Yen RWK, Falco JP, Hamilton SR, Baylin SB . 1990 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 3470–3474
Esteller M, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Rosell R, Sidransky D, Baylin SB, Herman JG . 1999 Cancer Res. 59: 67–70
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myohanen S, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 9821–9826
Inbal B, Cohen O, Polak-Charcon S, Kopolovic J, Vadal Ezra, Eisenbach L, Kimchi A . 1997 Nature 390: 180–184
Issa JPJ, Baylin SB, Belinsky SA . 1996 Cancer Res. 56: 3655–3658
Jones PA, Buckley JD . 1990 Adv. Cancer Res. 54: 1–23
Jones PL, Veenstra GC, Wade PA, Vermaak D, Kass SU, Landsberger N, Strouboulis J, Wolffe AP . 1998 Nature Genet. 19: 187–191
Kissil JL, Feinstein E, Cohen O, Jones PA, Tsai YC, Knowles MA, Edymann ME, Kimchi A . 1997 Oncogene 15: 403–407
Kissil JL, Kimchi A . 1998 Mol. Med. Today 4: 268–274
Katzenellenbogen RA, Baylin SB, Herman JG . 1999 Blood 93: 4347–4353
Laird PW, Jaenisch R . 1996 Annu. Rev. Genet. 30: 441–464
Li E, Bestor L, Jaenish R . 1992 Cell 69: 915–926
MacLeod AR, Rouleau J, Szyf M . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 11327–11337
Nelson HH, Christiani DC, Wiencke JK, Mark EJ, Wain JC, Kelsey KT . 1999 Cancer Res. 20: 667–674
Rouleau J, Macleod R, Szyf M . 1995 J. Biol. Chem. 270: 1595–1601
Sanchez-Cespedes MS. Esteller M, Wu L, Nawroz-Danish H, Yoo GH, Koch WM, Jen J, Herman JG, Sidransky D . 2000 Cancer Res. 60: 892–895
Tang X, Khuri FR, Lee JJ, Kemp BL, Liu D, Hong WK, Mao L . 2000 JNCI 92: 1511–1516
Vertino PM, Issa JP, Pereira-Smith OM, Baylin SB . 1994 Cell Growth Differ. 5: 1395–1402
Viallet J, Minna JD . 1990 Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2: 225–232
Wang X, Christiani DC, Wiencke JK, Fischbein M, Xu X, Cheng TJ, Mark E, Wain JC, Kelsey KT . 1995 Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 4: 543–548
Wu J, Issa JP, Herman J, Bassett DE, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB . 1990 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 8891–8895
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr Joe Brain, Dr David Hunter and Dr Howard Liber for helpful discussion. We also thank Linda Lineback, Lucy-Ann Principe, Marlys Rogers and David Miller. We thank Dr Eric Duell for helping statistical analysis and Drs Ed Azzam and John B Little for kindly providing NCI H209 cell line. This work was supported by CA08357 CA74386; ES/CA 06409, CA06717 and ES00002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DH., Nelson, H., Wiencke, J. et al. Promoter methylation of DAP-kinase: association with advanced stage in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 20, 1765–1770 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204302
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204302
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Aberrant hydroxymethylation in promoter CpG regions of genes related to the cell cycle and apoptosis characterizes advanced chronic myeloid leukemia disease, poor imatinib respondents and poor survival
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
Assessment of methylation status of locoregional lymph nodes in lung cancer using EBUS-NA
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2015)
-
Effect of cigarette smoke condensate on gene promoter methylation in human lung cells
Tobacco Induced Diseases (2014)
-
Transcription control of DAPK
Apoptosis (2014)
-
In silico epigenetic profiling of hypermethylated genes in non-small cell lung cancer
Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics (2014)