Abstract
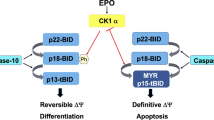
Activin A, one member of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β superfamily, is known to be a commitment factor for cell death and differentiation. In the present study, we demonstrate that human chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cell lines, KU812 and K562 cells, either induced apoptosis or differentiation, respectively, by treatment with activin A. During these cell fate decisive events caused by activin A, rapid and transient up-regulation of Mcl-1 was observed in both cell lines. In activin A-induced apoptosis of KU812 cells, continuous up-regulation of Bax was observed. After the decrease in Mcl-1 expression had occurred, activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 and cleavage of DFF45 were shown to take place in KU812 cells, resulting in the fragmentation of the genomic DNA of the cells. In contrast, the down-regulation of Mcl-1 without up-regulation of Bax caused accumulation of hemoglobin (Hb) contents in activin A-treated K562 cells. Interestingly, erythropoietin (EPO) prevented activin A-induced apoptosis with continuous expression of Mcl-1 and caused KU812 cells to undergo erythroid differentiation. To address the role of Mcl-1 in activin A-treated CML cells, KU812 and K562 cells were stably transfected with cDNA encoding Mcl-1 (designated as KU812/mcl and K562/mcl cells). As in combined effect of activin A and EPO on the parental KU812 cells, activin A induced differentiation, but not apoptosis, of KU812/mcl cells without modulating Bax levels. Activin A-treated K562/mcl cells, as well as parental cells, were only differentiated to erythroid cells. These results suggest that Mcl-1 is an early inducible gene activated by the activin A signaling pathway for both cellular differentiation and apoptosis, and continuous expression of Mcl-1 may be contributed to differentiation signals to the erythroid lineage in CML cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando T, Umezawa A, Suzuki A, Okita H, Sano M, Hiraoka Y, Aiso S, Saruta T and Hata J. . 1998 Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 89: 1326–1333.
Bilezikjian LM and Vale WW. . 1992 Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 3: 218–223.
Broxmeyer HE, Lu L, Cooper S, Schwall RH, Mason AJ and Nikolics K. . 1988 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 9052–9056.
Champlin RE and Golde DW. . 1985 Blood 65: 1039–1047.
Chao JR, Wang JM, Lee SF, Peng HW, Lin YH, Chou CH, Li JC, Huang HM, Chou CK, Kuo ML, Yen JJY and Yen HFY. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 4883–4898.
DePaolo LV, Bicsak TA, Erickson GF, Shimasaki S and Ling N. . 1991 Proc. Soc Exp. Biol. Med. 198: 500–512.
Eto Y, Tsuji T, Takezawa M, Takano S, Yokogawa Y and Shibai H. . 1987 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 142: 1095–1103.
Frigon Jr NL, Shao L-E, Young AL, Maderazo L and Yu J. . 1992 Blood 79: 765–772.
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ. . 1999 Gene Dev. 13: 1899–1911.
Haseyama Y, Sawada K, Oda A, Koizumi K, Takano H, Tarumi T, Nishio M, Handa M, Ikeda Y and Koike T. . 1999 Blood 94: 1568–1577.
Koseki T, Yamato K, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Tsujimoto Y and Nishihara T. . 1995 FEBS Lett. 376: 247–250.
Kozopas KM, Yang T, Buchan HL, Zhou P and Craig RW. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 3516–3520.
Kroemer G. . 1997 Nat. Med. 3: 614–620.
Kroemer G and Reed JC. . 2000 Nat. Med. 6: 513–519.
Lebrun JJ and Vale WW. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 1682–1691.
Li JP, D'Andrea A, Lodish HF and Baltimore D. . 1990 Nature 343: 762–764.
Ling N, Ying SY, Uemo N, Shimasaki S, Esch F, Hotta M and Guillemin R. . 1986 Nature 321: 779–782.
Los M, Wesselborg S and Schulze-Osthoff K. . 1999 Immunity 10: 629–639.
Mather JP, Woodruff TK and Krummen LA. . 1992 Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 201: 15.
Miyamoto Y, Kosaka M, Eto Y, Shibai H and Saito S. . 1990 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168: 1149–1156.
Mizuguchi T, Kosaka M and Saito S. . 1993 Blood 81: 2891–2897.
Moulding DA, Quayle JA, Hart CA and Edwards SW. . 1998 Blood 92: 2495–2502.
Murata M, Eto Y, Shibai H, Sakai M and Muramatsu M. . 1988 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 2434–2438.
Nishihara T, Okahashi N and Ueda N. . 1993 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197: 985–991.
Nishimura M, Kaku K, Azuno Y, Okafuji K, Etoh Y, Shiozaki M, Sasaki H, Inoue T and Kaneko T. . 1991 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 181: 1042–1047.
Peters R, Leyvraz S and Perey L. . 1998 Blood 92: 2041–2052.
Reynolds JE, Yang T, Qian L, Jenkinson JD, Zhou P, Eastman A and Craig RW. . 1994 Can. Res. 54: 6348–6352.
Sato T, Hanada M, Bodrug S, Irie S, Iwama N, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Golemis E, Fong L, Wang H-G and Reed JC. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 9238–9242.
Shao L-E, Frigon Jr NL, Young AL, Yu AL, Mathews LS, Vaughan J, Vale W and Yu J. . 1992 Blood 79: 773–781.
Shimizu S, Konishi A, Kodama T and Tsujimoto Y. . 2000 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 3100–3105.
Shiozaki M, Kosaka M and Eto Y. . 1998 Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 242: 631–635.
Smithgall TE, Briggs SD, Schreiner S, Lerner EC, Cheng H and Wilson MB. . 2000 Oncogene 19: 2612–2618.
Talpaz M and Kantarjian H. . 1995 Ann. Intern. Med. 122: 728–729.
Vale W, Rivier J, Vaughan J, McClintock R, Corrigan A, Wood W, Karr D and Spiess J. . 1986 Nature 321: 776–779.
Vander Heiden MG and Thompson CB. . 1999 Nat. Cell Biol. 1: E209–E216.
Wang JM, Chao JR, Chen W, Kuo ML, Yen JJ and Yang-yen HF. . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 6195–6206.
Yamashita T, Shimizu T and Ogata E. . 1991 J. Biol. Chem. 266: 3888–3892.
Yamato K, Koseki T, Kizaki M, Ikeda Y and Nishihara T. . 1996 Jpn. J. Clin. Hematol. 37: 564–567.
Yamato K, Koseki T, Ohguchi M, Kizaki M, Ideka Y and Nishihara T. . 1997 Mol. Endocrinol. 11: 1044–1052.
Yang E and Korsmeyer SJ. . 1996 Blood 88: 386–401.
Yang T, Kozopas KM and Craig RW. . 1995 J. Cell. Biol. 128: 1173–1184.
Yang T, Buchan HL, Townsend KJ and Craig RW. . 1996 J. Cell. Physiol. 166: 523–536.
Yu J, Shao L, Lemas V, Yu AL, Vaughan J, Rivier J and Vale W. . 1987 Nature 330: 765–767.
Yu J, Shao L-E, Vaughan J, Vale W and Yu AL. . 1989 Blood 73: 952–960.
Zhou P, Quan L, Kozopas KM and Craig RW. . 1997 Blood 89: 630–643.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Y Eto (Central Research Laboratory, Ajinomoto Co., Inc., Kawasaki, Japan) for providing recombinant human activin A, and J Ozawa for technical assistance. This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan, and the National Grant-in-Aid for the Establishment of a High-Tech Research Center in a Private University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuchi, Y., Kizaki, M., Yamato, K. et al. Mcl-1, an early-induction molecule, modulates activin A-induced apoptosis and differentiation of CML cells. Oncogene 20, 704–713 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204142
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204142
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacologic targeting of the P-TEFb complex as a therapeutic strategy for chronic myeloid leukemia
Cell Communication and Signaling (2021)
-
Aspirin has a better effect on PIK3CA mutant colorectal cancer cells by PI3K/Akt/Raptor pathway
Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Use of the relative release index for histamine in LAD2 cells to evaluate the potential anaphylactoid effects of drugs
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
The MEK inhibitor PD184352 enhances BMS-214662-induced apoptosis in CD34+ CML stem/progenitor cells
Leukemia (2011)
-
Bone morphogenetic protein and activin signaling in colorectal cancer
Current Colorectal Cancer Reports (2008)