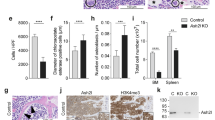
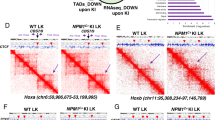
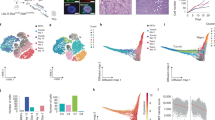
Abstract
Specific Hox genes are implicated in leukemic transformation, and their selective genetic collaboration with TALE homeobox genes, Pbx and Meis, accentuates their oncogenic potential. The molecular mechanisms underlying these coordinate functions, however, have not been characterized. In this study, we demonstrate that HoxA9 requires its Pbx interaction motif as well as its amino terminus to enhance the clonogenic potential of myeloid progenitors in vitro. We further show that HoxA9 forms functional trimeric DNA binding complexes with Pbx and Meis-like proteins on a modified enhancer. DNA binding complexes containing HoxA9 and TALE homeoproteins display cooperative transcriptional activity and are present in leukemic cells. Trimeric complex formation on its own, however, is not sufficient for HoxA9-mediated immortalization. Rather, structure-function analyses demonstrate that domains of HoxA9 which are necessary for cellular transformation are coincident with those required for trimer-mediated transcriptional activation. Furthermore, the amino terminus of HoxA9 provides essential transcriptional effector properties and its requirement for myeloid transformation can be functionally replaced by the VP16 activation domain. These data suggest that biochemical interactions between HoxA9 and TALE homeoproteins mediate cellular transformation in hematopoietic cells, and that their transcriptional activity in higher order DNA binding complexes provides a molecular basis for their collaborative roles in leukemogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthelsen J, Zappavigna V, Ferretti E, Mavilio F and Blasi F. . 1998 EMBO J. 5: 1434–1445.
Berthelsen J, Kilstrup-Nielsen C, Blasi F, Mavilio F and Zappavigna V. . 1999 Genes Dev. 13: 946–953.
Bischof LJ, Kagawa N, Moskow JJ, Takahashi Y, Iwamatsu A, Buchberg AM and Waterman MR. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 7941–7948.
Borrow J, Shearman AM, Stanton Jr VP, Becher R, Collins T et al. 1996 Nature Genet. 12: 159–167.
Bürglin TR. . 1997 Nucl. Acid Res. 25: 4173–4180.
Chang C-P, Shen W-F, Rozenfeld S, Lawrence HJ, Largman C and Cleary ML. . 1995 Genes Dev. 9: 663–674.
Chang C-P, Jacobs Y, Nakamura T, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG and Cleary ML. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 5679–5687.
Gonzales-Crespo S, Abu-Shaar M, Torres M, Martines-Arias C, Mann R and Morata G. . 1998 Nature 394: 196–200.
Hawley RG, Lieu FHL, Fong AZC and Hawley TS. . 1994 Gene Ther. 1: 136–138.
Jacobs Y, Schnabel CA and Cleary ML. . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. (In press).
Kasper L, Brindle P, Schnabel CA, Pritchard C, Cleary M and van Deursen J. . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 764–776.
Knoepfler PS and Kamps MP. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 5811–5819.
Knoepfler PS, Calvo KR, Chen H, Antonarakis SE and Kamps MP. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 14553–14558.
Kroon E, Krosl J, Thorsteinsdottir U, Baban S, Buchberg AM and Sauvageau G. . 1998 EMBO J. 13: 3714–3725.
Krosl J, Baban S, Krosl G, Rozenfeld S, Largman C and Sauvageau G. . 1998 Oncogene 16: 3403–3412.
Krumlauf R. . 1994 Cell 78: 191–201.
Lavau C, Szilvassy S, Slany R and Cleary ML. . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 4226–4237.
Lawrence HJ, Sauvageau G, Humphries RK and Largman C. . 1996 Stem Cells 14: 281–291.
Lu Q, Knoepfler PS, Scheele J, Wright DD and Kamps MP. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 3786–3795.
Maconochie MK, Nonchev S, Studer M, Chan S-K, Pöpperl H, Sham MH, Mann RS and Krumlauf R. . 1997 Genes Dev. 11: 1885–1895.
Magli MC, Barba P, Celetti A, De Vita G, Cillo C and Boncinelli E. . 1991 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 6348–6352.
Magli C, Largman C and Lawrence HJ. . 1997 J. Cell. Phys. 173: 168–177.
Mann RS and Affolter M. . 1998 Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 8: 423–429.
Monica K, Galili N, Nourse J, Saltman D and Cleary ML. . 1991 Mol. Cell. Biol. 11: 6149–6157.
Moskow JJ, Bullrich F, Huebner K, Daar IO and Buchberg AM. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 5434–5443.
Nakamura T, Jenkins NA and Copeland NG. . 1996a Oncogene 13: 2235–2242.
Nakamura T, Largaespada DA, Lee MP, Johnson LA, Ohyashiki K et al. 1996b Nature Genet. 12: 154–158.
Nakamura T, Largaespada DA, Shaughnessy Jr JD, Jenkins NA and Copeland NG. . 1996c Nature Genet. 12: 149–153.
Pear W, Nolan G, Scott M and Baltimore D. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 8392–8396.
Phelan ML, Rambaldi I and Featherstone MS. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 3989–3997.
Piper D, Bachelor A, Chang C-P, Cleary ML and Wolberger C. . 1999 Cell 96: 587–597.
Sauvageau G, Lansdorp PM, Eaves CJ, Hogge DE, Dragowska WH, Reid DS, Largman C, Lawrence HJ and Humphries RK. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 12223–12227.
Schnabel CA and Abate-Shen C. . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 2678–2688.
Shen W-F, Montgomery JC, Rozenfeld S, Moskow JJ, Lawrence HJ, Buchberg AM and Largman C. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 6448–6458.
Shen W-F, Rozenfeld S, Kwong A, Komuves LG, Lawrence HJ and Largman C. . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 3051–3061.
Swift GH, Liu Y, Rose SD, Bischof LJ, Steelman S, Buchberg AM, Wright CVE and MacDonald RJ. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 5109–5120.
Acknowledgements
These studies were supported by grants from the NIH (CA42971, AI-07290 and CA09151). CA Schnabel is a postdoctoral fellow of the Leukemia Society of America. We thank Bich-Tien Rouse for expert assistance in preparation of the HoxA9 monoclonal antibody. Neal Copeland for the Meis1a and HoxA9 cDNAs and the M1 and B112 cell lines, and J van Deursen for the VP16-HoxA9 cDNA. We also thank Phil Achacoso and Gary Nolan for the ΦNX packaging cell line.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schnabel, C., Jacobs, Y. & Cleary, M. HoxA9-mediated immortalization of myeloid progenitors requires functional interactions with TALE cofactors Pbx and Meis. Oncogene 19, 608–616 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203371
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203371
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of HOXA9 in solid tumors: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potential
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
The leukemogenicity of Hoxa9 depends on alternative splicing
Leukemia (2014)
-
HOX genes regulate Rac1 activity in hematopoietic cells through control of Vav2 expression
Leukemia (2013)
-
miRNA let-7c promotes granulocytic differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia
Oncogene (2013)
-
Distinct regulation of c-myb gene expression by HoxA9, Meis1 and Pbx proteins in normal hematopoietic progenitors and transformed myeloid cells
Blood Cancer Journal (2012)