Abstract
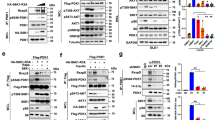
Akt is stimulated by several growth factors, and mediates their cell survival signals. Recent studies have shown that Akt may play an intermediate role between phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and p70 S6 kinase (p70S6K). Here we show that a novel nuclear p70S6K-related kinase (SRK) exists and that its in vivo function is also augmented by over-expression of Akt. Conceptual translation of the SRK cDNA revealed that the catalytic domain of SRK was highly homologous to that of p70S6K, and that the treatment of wortmannin or rapamycin strongly inhibited the phosphorylation and the activation of SRK, as in p70S6K. However, the N- and C-terminal domains of SRK were quite different from those of p70S6K. In immunolocalization analyses, we demonstrated a constitutive nuclear localization of SRK and the presence of a nuclear localization signal in its C-terminus. In vitro S6 phosphotransferase activities of SRK were stimulated with a slower kinetics by a variety of agonists to p70S6K. Interestingly, over-expression of the proto-oncogene Akt resulted in EGF-independent activation of SRK, while over-expression of kinase-dead Akt actually had an inhibitory effect. This relationship between Akt and SRK suggests that SRK may be a novel target of Akt and perhaps an important downstream component in the nuclear function of Akt.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi DR, Kozlowski MT, Weng QP, Morrice M and Avruch J. . 1997 Curr. Biol. 8: 69–81.
Alessi DR and Cohen P. . 1998 Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 8: 55–62.
Anderson KE, Coadwell J, Stephens LR and Hawkins PT. . 1998 Curr. Biol. 8: 684–691.
Andjelkovic M, Alessi DR, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb NJ, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucocq JM and Hemmings BA. . 1997 J. Biol. Chem. 272: 31515–31524.
Burgering BM and Coffer PJ. . 1995 Nature (London) 376: 599–602.
Burnett PE, Barrow RK, Cohen NA, Snyder SH and Sabatini DM. . 1998a Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 1432–1437.
Burnett PE, Blackshaw S, Lai MM, Qureshi IA, Burnett AF, Sabatini DM and Snyder SH. . 1998b Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 8351–8356.
Chou MM and Blenis J. . 1996 Cell 85: 573–583.
Chung J, Kuo CJ, Crabtree GR and Blenis J. . 1992 Cell 69: 1227–1236.
Chung J, Grammar TC, Lemon KP, Kazlauskas A and Blenis J. . 1994 Nature (London) 370: 71–75.
De Groot RP, Ballou LM and Sassone-Corsi P. . 1994 Cell 79: 81–91.
Gout I, Minami T, Hara K, Tsujishita Y, Filonenko V, Waterfield MD and Yonezawa K. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 30061–30064.
Kohn AD, Takeuchi F and Roth RA. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 21920–21926.
Lane HA, Fernandez A, Lamb NJC and Thomas G. . 1993 Nature (London) 363: 170–172.
Lee HK, Lee YK, Park SH, Kim YS, Park SH, Lee JW, Kwon HB, Soh J, Moore DD and Choi HS. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 14398–14402.
Pullen N, Dennis PB, Andjelkovic M, Dufner A, Kozma SC, Hemmings BA and Thomas G. . 1998 Science 279: 707–710.
Reinhard C, Fernandez A, Lamb NJC and Thomas G. . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 1557–1565.
Shima H, Pende M, Chen Y, Fumagalli S, Thomas G and Kozma SC. . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 6649–6659.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs H Ha, PJ Coffer, DR Alessi and J Blenis for reagents. This investigation was supported by a grant (971-0503-016-2) from the KOSEF and a grant (#HMP-97-M-2-0017) of the Good Health R&D Project from the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea. H-S Choi is supported by a grant from KOSEF through the Hormone Research Center. The sequence reported in this paper has been deposited in the GenBank data base (accession no.: AF099739).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koh, H., Jee, K., Lee, B. et al. Cloning and characterization of a nuclear S6 kinase, S6 kinase-related kinase (SRK); A novel nuclear target of Akt. Oncogene 18, 5115–5119 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202895
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202895
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Locus Mapping, Molecular Cloning, and Expression Analysis of rps6kb2, a Novel Metamorphosis-Related Gene in Chinese Tongue Sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis)
Marine Biotechnology (2017)
-
S6K2
AfCS-Nature Molecule Pages (2008)
-
Regulation of catalytic activity of S6 kinase 2 during cell cycle
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2007)
-
When translation meets transformation: the mTOR story
Oncogene (2006)
-
The Rb-family protein p107 inhibits translation by a PDK1-dependent mechanism
Oncogene (2002)