Abstract
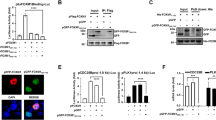
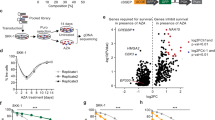
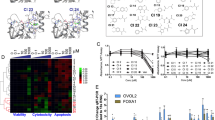
The p16-cyclin D-pRB-E2F pathway is frequently deregulated in human tumors. This critical regulatory pathway controls the G1/S transition of the mammalian cell cycle by positive and negative regulation of E2F-responsive genes required for DNA replication. To assess the value of the transcription factors E2Fs as targets for antiproliferative strategies, we have initiated a program aiming to develop inhibitors targeting specifically these proteins in vitro and in vivo. The cellular activity of E2F is the result of the heterodimeric association of two families of proteins, E2Fs and DPs, which then bind DNA. Here, we use a two hybrid approach to isolate from combinatorial libraries peptide aptamers that specifically interact with E2Fs DNA binding and dimerization domains. One of these is a potent inhibitor of E2F binding activity in vitro and in mammalian fibroblasts, blocks cells in G1, and the free variable region from this aptamer has the same effect. Our experiments argue that the variable region of this aptamer is structured, and that it functions by binding E2F with a motif that resembles a DP heterodimerization region, and blocking E2F's association with DP. These results show that cell proliferation can be inhibited using genetically-selected synthetic peptides that specifically target protein-protein interaction motifs within cell cycle regulators. These results also emphasize the critical role of the E2F pathway for cell proliferation and might allow the design of novel antiproliferative agents targeting the cyclin/CDK-pRB-E2F pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandara L, Buck V, Zamanain M, Johnson L and La Thangue N. . 1993 EMBO J. 12: 4317–4324.
Bandara L, Girling R and La Thangue N. . 1997 Nature Biotechn. 15: 896–901.
Cohen B, Colas P and Brent R. . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 14272–14277.
Colas P, Cohen B, Jessen T, Grishina I, McCoy J and Brent R. . 1996 Nature 380: 548–550.
Counillon L, Scholtz W, Lang J and Pouyssegur J. . 1993 Molec. Pharmacology 44: 1041–1045.
De Gregori J, Kowalik T and Nevins J. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 4215–4224.
Dobrowolski S, Stacey D, Harter M, Stine J and Hiebert S. . 1994 Oncogene 9: 2605–2612.
Duronio R and O'Farrel P. . 1995 Genes and Dev. 9: 1456–1468.
Fahraeus R, Paramio J, Ball K, Lain S and Lain D. . 1996 Curr. Biol. 6: 84–91.
Fields S and Song O-K. . 1989 Nature 340: 245–246.
Finley R and Brent R. . 1996 DNA cloning-Expression system: A practical approach Glover and Hames (eds). 6: pp 169–201.
Goodrich D, Wang N, Qian Y, Lee E and Lee W. . 1991 Cell 67: 293–302.
Gyuris J, Golemis E, Chertkov H and Brent R. . 1993 Cell 75: 791–803.
Hayashida W, Horiuchi M and Dzau V. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 21985–21992.
Helin K, Lees J, Vidal M, Dyson N, Harlow E and Fattaey A. . 1992 Cell 70: 337–350.
Helin K, Wu C, Fattaey A, Lees J, Dynlacht B, Ngwu C and Harlow E. . 1993 Genes Dev. 7: 1850–1861.
Johnson D, Schwarz J, Cress W and Nevins J. . 1993 Nature 365: 349–352.
Kolonin M and Finley R. . 1998 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 14266–14271.
Kowalik T, De Gregori J, Schwarz J and Nevins J. . 1995 Virol. 69: 2491–2500.
Krek W, Livingston D and Shirodkar S. . 1993 Science 262: 1557–1760.
Lukas J, Petersen B, Holm K, Bartek J and Helin K. . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 1047–1057.
Lamb N, Fernandez A, Watrin A, Labbé J-C and Cavadore C. . 1990 Cell 60: 151–165.
Mann D and Jones N. . 1996 Current. Biol. 4: 474–483.
Morishita R, Gibbons G, Horiuchi M, Ellison E, Nakama M, Zhang L, Kaneda Y, Ogihara T and Dzau VJ. . 1995 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 5855–5859.
Pages G, Lenormand P, L'Allemain G, Chambard J-C, Meloche S and Pouysségur J. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 8319–8323.
Qin X, Livingston D, Kaelin W, Adams P. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 10918–10922.
Sardet C, Franchi A and Pouyssegur J. . 1989 Cell 56: 271–280.
Sardet C, Vidal M, Cobrinik D, Geng Y, Onufryk C, Chen A and Weinberg R. . 1995 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 2403–2407.
Sardet C, Le Cam L, Fabbrizio E and Vidal M. . 1997 Oncogene as transcriptional regulators. In: Progress in gene expression (Birkhauser Yaniv M Ghysdael J (eds) 2: 1–63.
Shan B and Lee W. . 1994 Mol. Cell. Biol. 14: 8166–8173.
Shan B, Durfee T and Lee W. . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 679–684.
Sherr C. . 1996 Science 274: 1672–1677.
Slansky JE, Farnham PJ. . 1996 Curr. Opin. Microbiol. Immunol. 208: 1–30.
Vidal M, Braun P, Chen E, Boeke J and Harlow E. . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 19–24.
Weinberg R. . 1995 Cell 81: 323–330.
Weintraub S, Chow K, Luo R, Zhang S, He S and Dean D. . 1995 Nature 375: 812–815.
Wu C, Classon M, Dyson N and Harlow E. . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 3698–3706.
Xu W, Mendelsohn A and Brent R. . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 12473–12478.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Pierre Colas for invaluable comments and helpful discussion during this work and N Taylor for improving the quality of this manuscript. EF is a fellow of the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC). JP is supported by a Boehringer Ingelheim fellowship. RB's work is supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the US NIH. Work in the CS lab was supported by the ARC, by the CNRS (ATIPE no°3) and by the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM/`aides à l'implantation de nouvelles équipes').
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fabbrizio, E., Le Cam, L., Polanowska, J. et al. Inhibition of mammalian cell proliferation by genetically selected peptide aptamers that functionally antagonize E2F activity. Oncogene 18, 4357–4363 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202825
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202825
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Membrane cholesterol mediates the cellular effects of monolayer graphene substrates
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Suppression of FOXM1 Transcriptional Activities via a Single-Stranded DNA Aptamer Generated by SELEX
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Established and new mouse models reveal E2f1 and Cdk2 dependency of retinoblastoma, and expose effective strategies to block tumor initiation
Oncogene (2012)
-
Peptide aptamers as new tools to modulate clathrin-mediated internalisation — inhibition of MT1-MMP internalisation
BMC Cell Biology (2010)
-
E2F-1 as an anticancer drug target
Oncology Reviews (2009)