Abstract
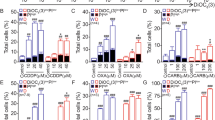
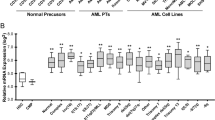
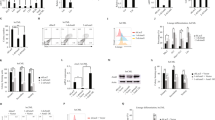
Vanadate (10 μM), a potent inhibitor of tyrosine phosphatase, added simultaneously potentiated BuONa-induced (1 mM) apoptosis. The steady-state level of nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA and the total cellular nucleophosmin/B23 protein decreased during the BuONa/vanadate-induced apoptosis. Stabilization and promotor transcriptional activity assays indicate that the decrease in nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA in BuONa/vanadate-treated HL-60 cells was transcriptionally regulated. A decline in telomerase activity was observed in HL-60 cells treated with BuONa/vanadate for 24–96 h. There was virtually no decline of nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA nor the telomerase activities during the growth arrest by serum-starvation. The decrease in nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA expression and telomerase activity in HL-60 cells subsequent to BuONa/vanadate treatment can thus be attributed to cellular apoptosis rather than the growth arrest induced by BuONa/vanadate. Nucleophosmin/B23 antisense oligomer treatment significantly potentiated BuONa-induced apoptosis and inhibition of telomerase activity. Results of this study suggest that nucleophosmin/B23 is one of the key elements in the down-regulation of nucleolar function for cellular apoptosis and mortalization.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Yung, B. Mortalization of human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells to be more susceptible to sodium butyrate-induced apoptosis and inhibition of telomerase activity by down-regulation of nucleophosmin/B23. Oncogene 17, 3055–3064 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202234
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202234
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
New insights into the biology of acute myeloid leukemia with mutated NPM1
International Journal of Hematology (2019)
-
Conjugated Polyelectrolyte Materials for Promoting Progenitor Cell Growth Without Serum
Scientific Reports (2013)
-
Cucurbitacin B inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation through disruption of microtubule polymerization and nucleophosmin/B23 translocation
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2012)
-
Involvement of PKC in TPA-potentiated apoptosis induction during hemin-mediated erythroid differentiation in K562 cells
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2009)
-
Involvement of nucleophosmin/B23 in TPA-induced megakaryocytic differentiation of K562 cells
British Journal of Cancer (2003)