Abstract
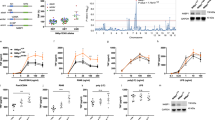
The transcription factor NF-κB is normally sequestered in the cytoplasm by its inhibitory subunit IκB. Most extracellular signals activate NF-κB through a mechanism involving the phosphorylation and proteasome-dependent degradation of IκB. EGF activates NF-κB in A-431 carcinoma cells, which overexpress EGF receptors and in mouse embryo fibroblasts, which have a normal complement of receptors. Supershift experiments indicate that the NF-κB complexes induced by EGF are composed of p50/p50 homodimers and p65/p50 heterodimers, but not c-rel. EGF stimulation enhances the degradation of IκBα, but not IκBβ nor an N-terminal deletion mutant of IκBα. Treatment of cells with a proteasome inhibitor, such as ALLN or MG132, blocks EGF-mediated NF-κB activation, indicating that EGF-induced NF-κB activation requires proteasome-dependent IκB degradation. Also, Bapta A/M (a cell-permeable chelator of intracellular calcium) blocks EGF-induced NF-κB activation and IκBα degradation, suggesting a requirement of intracellular free Ca2+ for this growth factor response. Protein kinase C inhibition, in contrast, did not influence EGF activation of NF-κB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Carpenter, G. Epidermal growth factor activation of NF-κB is mediated through IκBα degradation and intracellular free calcium. Oncogene 16, 2095–2102 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201731
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201731
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
PTEN inhibitor bpV(HOpic) confers protection against ionizing radiation
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Simultaneous targeting of HER family pro-survival signaling with Pan-HER antibody mixture is highly effective in TNBC: a preclinical trial with PDXs
Breast Cancer Research (2020)
-
An LGG-derived protein promotes IgA production through upregulation of APRIL expression in intestinal epithelial cells
Mucosal Immunology (2017)
-
Store-operated Ca2+ Entry Facilitates the Lipopolysaccharide-induced Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Gastric Cancer Cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
NF-κB signaling pathways regulated by CARMA family of scaffold proteins
Cell Research (2011)