Abstract
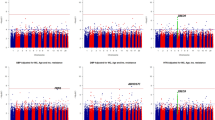
Essential hypertension (EH) is thought to be a polygenic disease. Several candidate genes of this disease have been investigated in studies using polymorphic genetic markers, but some studies have failed to show any association of EH with these genes. In this experiment, we used microsatellite markers on chromosome 1, and performed an association study between EH and control subjects. Genomic DNA was amplified with fluorescently labelled primers from the Applied Biosystems PRISM linkage mapping set HD-5 comprising 63 highly polymorphic microsatellite markers with an average spacing of 4.5 cM. We isolated three loci showing significant differences: D1S507, D1S2713 and D1S2842. The P-values of the allele with the greatest post hoc contributions in D1S507, D1S2713 and D1S2842 were 0.0008, 0.0062 and 0.0084, respectively. All these values were significant after Bonferroni correction. Furthermore, we found that the three microsatellite alleles were associated with the levels of systolic blood pressure. These data suggest that there are at least the three susceptibility loci for EH on chromosome 1, and that a case–control study using microsatellite markers on genomewide basis is a useful method for isolating the susceptibility loci of multifactorial disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong Y et al. Genetic and environmental influences on blood pressure in elderly twins. Hypertension 1994; 24: 663–670.
Samani NJ . Genome scans for hypertension and blood pressure regulation. Am J Hypertens 2003; 16: 167–171.
Rice T et al. Genome-wide linkage analysis of systolic and diastolic blood pressure: the Quebec Family Study. Circulation 2000; 102: 1956–1963.
Perola M et al. Genome-wide scan of predisposing loci for increased diastolic blood pressure in Finnish siblings. J Hypertens 2000; 18: 1579–1585.
Harrap SB et al. Blood pressure QTLs identified by genome-wide linkage analysis and dependence on associated phenotypes. Physiol Genomics 2002; 8: 99–105.
Hunt SC et al. Genome scans for blood pressure and hypertension: the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Family Heart Study. Hypertension 2002; 40: 1–6.
Thiel BA et al. A genome-wide linkage analysis investigating the determinants of blood pressure in whites and African Americans. Am J Hypertens 2003; 16: 151–153.
Rahmutula D et al. Association study between the variants of the human ANP Gene and essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 2001; 24: 291–294.
Nakayama T et al. Nucleotide sequence of the 5′-flanking region of the type A human natriuretic peptide receptor gene and association analysis using a novel microsatellite in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1999; 12: 1144–1148.
Nakayama T et al. Functional deletion mutation of the 5′-flanking region of the type A human natriuretic peptide receptor gene and its association with essential hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy in the Japanese. Circ Res 2000; 86: 841–845.
Nakayama T et al. A novel missense mutation of exon 3 in the type A human natriuretic peptide receptor gene: possible association with essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 395–401.
Jeunemaitre X et al. Molecular basis of human hypertension: role of angiotensinogen. Cell 1992; 71: 169–180.
Hasimu B et al. Haplotype analysis of the human renin gene and essential hypertension. Hypertension 2003; 41: 308–312.
Neuhauser M . Exact tests for the analysis of case–control studies of genetic markers. Hum Hered 2002; 54: 151–156.
Elston RC . Linkage and association. Genet Epidemiol 1998; 15: 565–576.
Nakayama T et al. Haplotype analysis of the prostacyclin synthase gene and essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 2003; 26: 553–557.
Nakayama T et al. Isolation of the 5′-flanking region of genes by thermal asymmetric interlaced polymerase chain reaction. Med Sci Monit 2001; 7: 345–349.
Dib C et al. A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature 1996; 380: 152–154.
Nakayama T et al. Association analysis of CA repeat polymorphism of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene with essential hypertension in Japanese. Clin Genet 1997; 51: 26–30.
Sham PC, Curtis D . Monte Carlo tests for associations between disease and alleles at highly polymorphism loci. Ann Hum Genet 1995; 59: 97–105.
Risch N, Merikangas K . The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science 1996; 273: 1516–1517.
Edwards JH . The sib-pair problem. I. Affected pairs with parents. Constant penetrance models. Ann Hum Genet 1997; 61: 351–364.
Jones HB . The relative power of linkage and association studies for the detection of genes involved in hypertension. Kidney Int 1998; 53: 1446–1448.
Spielman RS, Ewens WJ . The TDT and other family-based tests for linkage disequilibrium and association. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 59: 983–989.
Kruglyak L . The use of a genetic map of biallelic markers in linkage studies. Nat Genet 1997; 17: 21–24.
Krushkal J et al. Genome-wide linkage analyses of systolic blood pressure using highly discordant siblings. Circulation 1999; 99: 1407–1410.
Xu X et al. An extreme-sib-pair genome scan for genes regulating blood pressure. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 64: 1694–1701.
Sharma P et al. A genome-wide search for susceptibility loci to human essential hypertension. Hypertension 2000; 35: 1291–1296.
Levy D et al. Evidence for a gene influencing blood pressure on chromosome 17. Genome scan linkage results for longitudinal blood pressure phenotypes in subjects from the Framingham heart study. Hypertension 2000; 36: 477–483.
Allayee H et al. Genome scan for blood pressure in Dutch dyslipidemic families reveals linkage to a locus on chromosome 4p. Hypertension 2001; 38: 773–778.
Kristjansson K et al. Linkage of essential hypertension to chromosome 18q. Hypertension 2002; 39: 1044–1049.
Angius A et al. A new essential hypertension susceptibility locus on chromosome 2p24–p25, detected by genomewide search. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 893–905.
Lander E, Kruglyak L . Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet 1995; 11: 241–247.
Caulfield M et al. Genome-wide mapping of human loci for essential hypertension. Lancet 2003; 361: 2118–2123.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms M Nakamura, Ms K Sugama, and Mr. N Sato for their technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan (High-Tech Research Center, Nihon University, Japan), a research grant from the alumni association of Nihon University School of Medicine and the Tanabe Biomedical Conference, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakayama, T., Soma, M., Kanmatsuse, K. et al. The microsatellite alleles on chromosome 1 associated with essential hypertension and blood pressure levels. J Hum Hypertens 18, 823–828 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001740
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001740
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 2 (P2RY2) gene associated with essential hypertension in Japanese men
Journal of Human Hypertension (2010)
-
Linkage mapping of CVD risk traits in the isolated Norfolk Island population
Human Genetics (2008)
-
A haplotype in the human Sur2 gene is associated with essential hypertension
Journal of Human Hypertension (2006)
-
Towards understanding the aetiology and pathophysiology of human hypertension: where are we now?
Journal of Human Hypertension (2006)