Abstract
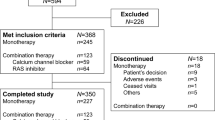
Objective: To evaluate the antihypertensive efficacy, tolerability, safety, and dose-response characteristics of the novel calcium antagonist, mibefradil, in combination with a diuretic regimen.Design: A multinational, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-design trial.Methods: Three hundred and seven patients whose mild-to-moderate essential hypertension remained uncontrolled after 4 weeks of treatment with hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 25 mg/day and placebo were randomised to receive combined treatment with HCTZ and once-daily doses of 12.5, 25, 50, or 100 mg of mibefradil or placebo. After 8 weeks of combined treatment, HCTZ was withdrawn and the mibefradil groups continued on their respective doses for an additional 6 weeks.Results: After 8 weeks, the addition of once-daily doses of mibefradil to the initial HCTZ regimen resulted in clinically relevant, dose-related reductions in sitting diastolic blood pressure (SDBP) and sitting systolic blood pressure (SSBP) at trough, which were significantly greater in the 50 and 100 mg dose groups compared to the placebo group (P ⩽ 0.003). Placebo-corrected treatment effects on SDBP and SSBP at the end of the combined treatment period relative to baseline were, respectively, −4.1 and −8.0 mm Hg in the 50 mg mibefradil group and −9.5 and −8.0 mm Hg in the 100 mg mibefradil group. Therapeutic response rates to combination mibefradil and HCTZ therapy were high and dose related, reaching 82% for SDBP in the 100 mg group. Conclusions: The addition of once-daily doses of 50 or 100 mg of mibefradil to patients whose hypertension is not controlled by HCTZ alone is well tolerated and effective in improving BP control.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carney, S., Wing, L., Ribeiro, A. et al. The addition of mibefradil to chronic hydrochlorothiazide therapy in hypertensive patients is associated with a significant antihypertensive effect. J Hum Hypertens 11, 459–466 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000465
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000465
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects of concomitant mibefradil-digoxin therapy at therapeutic doses
European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (1999)