Abstract
Objective:
To determine whether oestrogen receptor (ER)α messenger RNA (mRNA) levels or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are associated with obesity in Swedish women.
Design:
ERα mRNA expression levels were measured by real-time qPCR in subcutaneous adipose tissue from non-obese (N=16, BMI <30) and obese (N=17, BMI ⩾30) women. In addition, ERα mRNA expression levels were determined in isolated adipocytes. ERα promoter usage was characterized by 5′ RACE and by real-time qPCR in subcutaneous adipose tissue from the same non-obese and obese women. Two ERα SNPs were scored in 509 non-obese and 489 obese females.
Results:
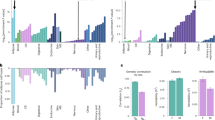
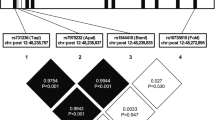
ERα mRNA expression levels were lower in obese compared to non-obese women in both subcutaneous adipose tissue and in adipocytes. We show that two ERα promoters are differentially utilized in obese and non-obese individuals. We did not find any significant association between obesity and the ERα SNPs or haplotypes assayed.
Conclusion:
The reduced ERα mRNA levels observed in adipose tissue from obese compared to non-obese women support a role for oestrogen signaling via ERα, in control of body weight. Mechanistic studies of the role of ERα in adipocytes and how its expression is regulated in relation to fat mass should be performed. The latter studies should focus on the two promoters that are used differently in obese and non-obese individuals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comuzzie AG, Williams JT, Martin LJ, Blangero J . Searching for genes underlying normal variation in human adiposity. J Mol Med 2001; 79: 57–70.
Clement K . Genetics of human obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 2005; 64: 133–142.
Matthews J, Gustafsson JA . Estrogen signaling: a subtle balance between ER alpha and ER beta. Mol Intervent 2003; 3: 281–292.
Green S, Walter P, Kumar V, Krust A, Bornert JM, Argos P et al. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature 1986; 320: 134–139.
Greene GL, Gilna P, Waterfield M, Baker A, Hort Y, Shine J . Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science 1986; 231: 1150–1154.
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA . Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 5925–5930.
Flouriot G, Brand H, Denger S, Metivier R, Kos M, Reid G et al. Identification of a new isoform of the human estrogen receptor-alpha (hER-alpha) that is encoded by distinct transcripts and that is able to repress hER-alpha activation function 1. EMBO J 2000; 19: 4688–4700.
Dieudonne MN, Leneveu MC, Giudicelli Y, Pecquery R . Evidence for functional estrogen receptors alpha and beta in human adipose cells: regional specificities and regulation by estrogens. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2004; 286: C655–C661.
Blumel JE, Castelo-Branco C, Rocangliolo ME, Bifa L, Tacla X, Mamani L . Changes in body mass index around menopause: a population study of Chilean woman. Menopause 2001; 8: 239–244.
Lovejoy JC . The menopause and obesity. Prim Care 2003; 30: 317–325.
Ozbey N, Sencer E, Molvalilar S, Orhan Y . Body fat distribution and cardiovascular disease risk factors in pre- and postmenopausal obese women with similar BMI. Endocr J 2002; 49: 503–509.
Dicker A, Ryden M, Naslund E, Muehlen IE, Wiren M, Lafontan M et al. Effect of testosterone on lipolysis in human pre-adipocytes from different fat depots. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 420–428.
Haarbo J, Marslew U, Gotfredsen A, Christiansen C . Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy prevents central distribution of body fat after menopause. Metabolism 1991; 40: 1323–1326.
Gambacciani M, Ciaponi M, Cappagli B, Piaggesi L, De Simone L, Orlandi R et al. Body weight, body fat distribution, and hormonal replacement therapy in early postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 414–417.
Reubinoff BE, Wurtman J, Rojansky N, Adler D, Stein P, Schenker JG et al. Effects of hormone replacement therapy on weight, body composition, fat distribution, and food intake in early postmenopausal women: a prospective study. Fertil Steril 1995; 64: 963–968.
Manson JE, Hsia J, Johnson KC, Rossouw JE, Assaf AR, Lasser NL et al. Estrogen plus progestin and the risk of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 523–534.
Sites CK, L'Hommedieu GD, Toth MJ, Brochu M, Cooper BC, Fairhurst PA . The effect of hormone replacement therapy on body composition, body fat distribution, and insulin sensitivity in menopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 2701–2707.
Couse JF, Korach KS . Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev 1999; 20: 358–417.
Krege JH, Hodgin JB, Couse JF, Enmark E, Warner M, Mahler JF et al. Generation and reproductive phenotypes of mice lacking estrogen receptor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 15677–15682.
Lubahn DB, Moyer JS, Golding TS, Couse JF, Korach KS, Smithies O . Alteration of reproductive function but not prenatal sexual development after insertional disruption of the mouse estrogen receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 11162–11166.
Atwood LD, Heard-Costa NL, Cupples LA, Jaquish CE, Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB . Genomewide linkage analysis of body mass index across 28 years of the Framingham Heart Study. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1044–1050.
Fox CS, Heard-Costa NL, Wilson PW, Levy D, D’Agostino RB, Atwood Sr LD . Genome-wide linkage to chromosome 6 for waist circumference in the Framingham Heart Study. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1399–1402.
Okura T, Koda M, Ando F, Niino N, Ohta S, Shimokata H . Association of polymorphisms in the estrogen receptor alpha gene with body fat distribution. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27: 1020–1027.
Fox CS, Yang Q, Cupples LA, Guo CY, Atwood LD, Murabito JM et al. Sex-specific association between estrogen receptor-alpha gene variation and measures of adiposity: the Framingham Heart Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 6257–6262.
Lofgren P, Hoffstedt J, Ryden M, Thorne A, Holm C, Wahrenberg H et al. Major gender differences in the lipolytic capacity of abdominal subcutaneous fat cells in obesity observed before and after long-term weight reduction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 764–771.
Eriksson P, Reynisdottir S, Lonnqvist F, Stemme V, Hamsten A, Arner P . Adipose tissue secretion of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in non-obese and obese individuals. Diabetologia 1998; 41: 65–71.
Hoffstedt J, Arvidsson E, Sjolin E, Wahlen K, Arner P . Adipose tissue adiponectin production and adiponectin serum concentration in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1391–1396.
Bonora E, Targher G, Alberiche M, Bonadonna RC, Saggiani F, Zenere MB et al. Homeostasis model assessment closely mirrors the glucose clamp technique in the assessment of insulin sensitivity: studies in subjects with various degrees of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2000; 23: 57–63.
Reynisdottir S, Wahrenberg H, Carlstrom K, Rossner S, Arner P . Catecholamine resistance in fat cells of women with upper-body obesity due to decreased expression of beta 2-adrenoceptors. Diabetologia 1994; 37: 428–435.
Arvidsson E, Viguerie N, Andersson I, Verdich C, Langin D, Arner P . Effects of different hypocaloric diets on protein secretion from adipose tissue of obese women. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1966–1971.
Smith EP, Boyd J, Frank GR, Takahashi H, Cohen RM, Specker B et al. Estrogen resistance caused by a mutation in the estrogen-receptor gene in a man. N Engl J Med 1994; 331: 1056–1061.
Dahlman I, Eriksson P, Kaaman M, Jiao H, Lindgren CM, Kere J et al. alpha2-Heremans-Schmid glycoprotein gene polymorphisms are associated with adipocyte insulin action. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 1974–1979.
Kos M, Reid G, Denger S, Gannon F . Minireview: genomic organization of the human ERalpha gene promoter region. Mol Endocrinol 2001; 15: 2057–2063.
Okuda Y, Hirata S, Watanabe N, Shoda T, Kato J, Hoshi K . Novel splicing events of untranslated first exons in human estrogen receptor alpha (ER alpha) gene. Endocr J 2003; 50: 97–104.
Dahlman I, Linder K, Arvidsson Nordstrom E, Andersson I, Liden J, Verdich C et al. Changes in adipose tissue gene expression with energy-restricted diets in obese women. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 81: 1275–1285.
Gallicchio L, Visvanathan K, Miller SR, Babus J, Lewis LM, Zacur H et al. Body mass, estrogen levels, and hot flashes in midlife women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005; 193: 1353–1360.
Olson MB, Shaw LJ, Kaizar EE, Kelsey SF, Bittner V, Reis SE et al. Obesity distribution and reproductive hormone levels in women: A Report from the NHLBI-Sponsored WISE Study. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2006; 15: 836–842.
Acknowledgements
We thank all subjects for participating in the present study. This work was supported by The Royal Physiographic Society in Lund, Stiftelsen Goljes Minne, Stiftelsen Lars Hiertas Minne (all to MN) and the EU NoE CASCADE. The authors want to thank Patricia Humire, Eva Sjölin, Lise-Lotte Vedin and Kerstin Wåhlén for technical assistance. The authors are also greatful to Professor Anthony Wright and Doctor Knut Steffensen for critical comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nilsson, M., Dahlman, I., Rydén, M. et al. Oestrogen receptor α gene expression levels are reduced in obese compared to normal weight females. Int J Obes 31, 900–907 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803528
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803528
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hyperglycemia and O-GlcNAc transferase activity drive a cancer stem cell pathway in triple-negative breast cancer
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Obesity as a premature aging phenotype — implications for sarcopenic obesity
GeroScience (2022)
-
Estrogen-related mechanisms in sex differences of hypertension and target organ damage
Biology of Sex Differences (2020)
-
The rs2175898 Polymorphism in the ESR1 Gene has a Significant Sex-Specific Effect on Obesity
Biochemical Genetics (2020)
-
Inflammation increases MMP levels via PGE2 in human vascular wall and plasma of obese women
International Journal of Obesity (2019)