Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Data on the association of resistin levels with markers of insulin resistance are highly contrasting in humans and very few studies about its role in inflammation are available. This study investigates associations between serum resistin levels and markers of insulin resistance, inflammation (C-reactive protein (CRP)) and of oxidative stress (nytrotirosine (NT)).
SUBJECTS:
A randomly collected sample of 300 men from a population-based cohort was analysed, separated into two groups according to body mass index (BMI) and waist values.
RESULTS:
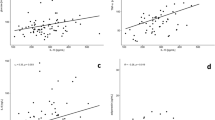
Correlations between resistin and BMI, waist, triglyceride, uric acid, fasting glucose, insulin and Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) values were significant in subjects with normal BMI, but not in overweight/obese subjects. In a multiple regression model, after multiple adjustments and exclusion of diabetic patients, only fasting glucose remained significantly associated with resistin levels. Otherwise, resistin is associated to CRP levels in all individuals, after multiple adjustments and exclusion of diabetic patients (in normal BMI β=0.82; 95% CI 0.21, 1.42; in overweight/obese β=0.43; 95% CI 0.10, 0.76). In the same model, resistin values are negatively related to NT levels in normal weight individuals (β=−1.61; 95% CI −0.77–2.45).
CONCLUSIONS:
Serum resistin is weakly associated with metabolic abnormalities in subjects with normal BMI, while in overweight/obese patients this correlation is not significant, perhaps due to the higher fat content in these subjects. Serum resistin is directly correlated with CRP and inversely to NT. An intriguing hypothesis, which needs to be tested, is that resistin is secreted in response to a chronic low-grade inflammation, and has antioxidant properties.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS, Lazar MA . The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001; 18: 307–312.
Steppan CM, Lazar MA . The current biology of resistin. J Intern Med 2004; 255: 439–447.
Ghosh S, Singh AK, Aruna B, Mukhopadhyay S, Ehtesham NZ . The genomic organization of mouse resistin reveals major differences from the human resistin: functional implications. Gene 2003; 305: 27–34.
Yang RZ, Huang Q, Xu A, McLenithan JC, Eison JA, Shuldiner AR, Alkan S, Gong DW . Comparative studies of resistin expression and phylogenomics in human and mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 310: 927–935.
Savage DB, Sewter CP, Klenk ES, Segal DG, Vidal-Puig A, Considine RV, O'Rahilly S . Resistin/FIZZ3 expression in relation to obesity and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ action in humans. Diabetes 2001; 50: 2199–2202.
Nagaev I, Smith U . Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are not related to resistin expression in human fat cells or skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 285: 561–564.
Fasshauer M, Klein J, Neumann S, Eszlinger M, Paschke R . Tumor necrosis factor α is a negative regulator of resistin gene expression and secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 288: 1027–1031.
McTernan CL, McTernan PG, Harte AL, Levick PL, Barnett AH, Kumar S . Resistin, central obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2002; 359: 46–47.
Janke J, Engeli S, Gorzelniak K, Luft FC, Sharma AM . Resistin gene expression in human adipocytes is not related to insulin resistance. Obes Res 2000; 10: 1–5.
Patel L, Buckels AC, Kinghorn IJ, Murdock PR, Holbrook JD, Plumpton C, Macphee CH, Smith SA . Resistin is expressed in human macrophages and directly regulated by PPARγ activators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 300: 427–476.
Fain JN, Cheema PS, Bahouth SW, Hiler ML . Resistin release by human adipose tissue explants in primary culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 300: 674–678.
Yannakoulia M, Yiannakouris N, Blüher S, Matalas AL, Klimis-Zacas D, Mantzoros CS . Body fat mass and macronutrient intake in relation to circulating soluble leptin receptor, free leptin index, adiponectin and resistin concentrations in healthy humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1730–1736.
Lee JH, Chan JL, Yiannakouris N, Kontogianni M, Estrada E, Seip R, Orlova C, Mantzoros CS . Circulating resistin levels are not associated with obesity or insulin resistance in humans and are not regulated by fasting or leptin administration: cross-sectional and interventional studies in normal, insulin-resistant, and diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 4848–4856.
McTernan PG, Fisher FM, Valsamakis G, Chetty R, Harte A, McTernan CL, Clark PMS, Smith SA, Barnett AH, Kumar S . Resistin and type 2 diabetes: regulation of resistin expression by insulin and rosiglitazone and the effects of recombinant resistin on lipids and glucose metabolism in human differentiated adipocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 6098–6106.
Youn BS, Yu KY, Park HJ, Lee NS, Min SS, Youn MY, Cho YM, Park YJ, Kim SY, Lee HK, Park KS . Plasma resistin concentrations measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a newly developed monoclonal antibody are elevated in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 150–156.
Pfutzner A, Kunt T, Hohberg C, Mondok A, Pahler S, Konrad T, Lübben G, Forst T . Fasting intact proinsulin is a highly specific predictor of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Care 2004; 27: 682–687.
Volarova de Courten B, Degawa-Yamauchi M, Considine RV, Tataranni PA . High serum resistin is associated with an increase in adiposity but not a worsening of insulin resistance in Pima Indians. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1279–1284.
Vendrell J, Broch M, Vilarrasa N, Molina A, Gomez JM, Gutierrez C, Simon I, Soler J, Richart C . Resistin, adiponectin, ghrelin, leptin and proinflammatory cytochines: relationships in obesity. Obes Res 2004; 12: 962–971.
Heilbronn LK, Rood J, Janderova L, Albu JB, Kelley DE, Ravussin E, Smith SR . Relationship between serum resistin concentrations and insulin resistance in nonobese, obese, and obese diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1844–1848.
Azuma K, Katsukawa F, Oguchi S, Murata M, Yamazaki H, Shimada A, Saruta T . Correlation between serum resistin level and adiposity in obese individuals. Obes Res 2004; 11: 997–1001.
Lu SC, Shieh WY, Chen CY, Hsu SC, Chen HL . Lipopolysaccharide increases resistin gene expression in vivo and in vitro. FEBS Lett 2002; 530: 158–162.
Kaser S, Kaser A, Sandhofer CF, Ebenbichler CF, Tilg H, Patsch JR . Resistin messanger-RNA is increased by proinflammatory cytokines in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 309: 286–290.
Shetty GK, Economides PA, Horton ES, Mantzoros CS, Veves A . Circulating adiponectin and resistin levels in relation to metabolic factors, inflammatory markers, and vascular reactivity in diabetic patients and subjects at risk for diabetes. Diabet Care 2004; 27: 2450–2457.
Smith SR, Bai F, Charbonneau C, Janderova L, Argyropoulos G . A promoter genotype and oxidative stress potentially link resistin to human insulin resistance. Diabetes 2003; 52: 1611–1618.
Felipe F, Bonet ML, Ribot J, Palou A . Modulation of resistin expression by retinoic acid and vitamin A status. Diabetes 2004; 53: 882–889.
National Institute of Health. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486–2497.
The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabet Care 2003; 26: S5–S20.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Saltin B, Grimby G . Physiological analysis of middle-aged and old former athletes. Comparison with still active athletes of the same ages. Circulation 1968; 38: 1104–1115.
Hotamisligil GS . The irresistible biology of resistin. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 173–174.
Zhang JL, Qin YW, Zheng X, Qiu JL, Zou DJ . Serum resistin level in essential hypertensive patients with different glucose tolerance. Diabet Med 2003; 20: 828–831.
Ridker PM, Wilson PWF, Grundy SM . Should C-reactive protein be added to metabolic syndrome and to assessment of global cardiovascular risk? Circulation 2004; 109: 2818–2825.
Reilly MP, Lehrke M, Wolfe ML, Rohatgi A, Lazar MA, Rader DJ . Resistin is an inflammatory marker of atherosclerosis in humans. Circulation 2005; 111: 932–939.
Lehrke M, Reilly MP, Millington SC, Iqbal N, Rader DJ, Lazar MA . An inflammatory cascade leading to hyperresistinemia in humans. PloS Med 2004; 1: e45.
Chu N, Kong APS, Kim DD, Armstrong D, Baxi S, Deutsch R, Caulfield M, Mudaliar SR, Reitz R, Henry RR, Reaven PD . Differential effects of metformin and troglitazone on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Care 2002; 25: 542–548.
Beckman JS, Koppenol WH . Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol 1996; 271: C1424–C1437.
Ceriello A, Mercuri F, Quagliaro L, Assaloni R, Motz E, Tonutti L, Taboga C . Detection of nitrotyrosine in the diabetic plasma: evidence of oxidative stress. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 834–838.
Ceriello A, Quagliaro L, Catone B, Pascon R, Piazzola M, Bais B, Marra G, Tonutti L, Taboga C, Motz E . Role of hyperglycemia in nitrotyrosine postprandial generation. Diabet Care 2002; 25: 1439–1443.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Dr Baldi Carla, Dr Benini Lorenzo, Dr Calosso Giovanni, Dr Dusio Ferruccio, Dr Forestiere Giuseppe, Dr Lucia Claudio, Dr Mangiameli Maria Pia, Dr Nuti Claudio and Dr Vergoni Ferdinando, for their precious assistance in performing the study. This study was supported by a grant from: Regione Piemonte, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bo, S., Gambino, R., Pagani, A. et al. Relationships between human serum resistin, inflammatory markers and insulin resistance. Int J Obes 29, 1315–1320 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803037
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803037
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Coenzyme Q10 supplementation improves adipokine profile in dyslipidemic individuals: a randomized controlled trial
Nutrition & Metabolism (2022)
-
Association of adiponectin, leptin and resistin with inflammatory markers and obesity in dementia
Biogerontology (2017)
-
Relation of resistin to proprotein convertase subtilisin–kexin type 9 levels in coronary artery disease patients with different nutritional status
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2015)
-
Whole-body cryostimulation as an effective method of reducing low-grade inflammation in obese men
The Journal of Physiological Sciences (2013)
-
Relations of Circulating Resistin and Adiponectin and Cardiac Structure and Function: The Framingham Offspring Study
Obesity (2012)