Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Obesity is linked to the insulin resistance syndrome (IRS), type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cardiovascular disease. Markers of chronic subclinical inflammation such as high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) are closely related to insulin resistance and obesity. Recent evidence suggests that adiponectin, a protein whose circulating levels are decreased in obesity, has anti-inflammatory properties, and also appears to enhance potently insulin action and therefore appears to function as a signal produced by adipose tissue that influences whole-body glucose metabolism.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS:
We investigated the cross-sectional and longitudinal association of adiponectin with CRP and IL-6 in 41 morbidly obese women with different stages of glucose tolerance before and 17 months after significant weight loss induced by gastric surgery. Adiponectin was measured by RIA. CRP and IL-6 were determined by commercially available ELISA systems.
RESULTS:
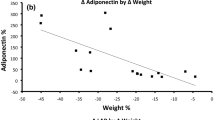
Weight loss induced a significant shift from T2D (preoperatively 34% vs postoperatively 2%) to impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) (37% preoperatively vs 30% postoperatively) and normal glucose tolerance (NGT) (29% preoperatively vs 68% postoperatively). Preoperatively adiponectin levels were negatively correlated with CRP (r=−0.59, P<0.0006), IL-6 (r=−0.42, P<0.02) and leukocytes (r=−0.41, P<0.007). After gastroplasty, adiponectin concentrations increased significantly (15.4±8.2 vs 19.8±6.2 μg/ml, P<0.005) associated with changes of weight and body mass index (r=−0.45, P<0.007; r=−0.35, P<0.04). Furthermore, preoperative CRP was significantly associated with changes in adiponectin even after adjustment for sex, age, preoperative body mass index (BMI) impaired glucose metabolism and changes in BMI and changes in BMI (standardized beta 0.61, P=0.005).
CONCLUSION:
Levels of adiponectin, which are associated with markers of chronic subclinical inflammation, could be significantly increased after weight loss in morbidly obese patients. This increase was more pronounced in patients with NGT compared to those with T2D and IGT. Preoperative levels of CRP are predictive for changes of adiponectin after weight loss.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
US Department of Health and Human Services. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: The Evidence Report, US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, NIH, NHLBI, 1998.
Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, Williamson DF, Thun MJ, Wood JL . The effect of age on the association between body-mass index and mortality. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 1–7.
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Stampfer MJ, Hennekens CH . Plasma concentration of interleukin-6 and the risk of future myocardial infarction among apparently healthy men. Circulation 2000; 101: 1767–1772.
Festa A, D'Agostino Jr R, Howard G, Mykkänen L, Tracy RP, Haffner S . Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome. The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Circulation 2000; 102: 42–47.
Kopp HP, Kopp CW, Festa A, Krzyzanowska K, Kriwanek S, Minar E, Roka R, Schernthaner G . Impact of weight loss on inflammatory proteins and their association with the insulin resistance syndrome in morbidly obese patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: 1042–1047.
Nicklas BJ, Ambrosius W, Messier SP, Miller GD, Penninx BW, Loeser RF, Palla S, Bleecker E, Pahor M . Diet-induced weight loss, exercise, and chronic inflammation in older, obese adults: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 4: 544–551.
Bastard JP, Jardel C, Bruckert E, Blondy P, Capeau J, Laville M, Vidal H, Hainque B . Elevated levels of interleukin 6 are reduced in serum and subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese women after weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 3338–3342.
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakalima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa . Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000; 20: 1595–1599.
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni A . Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1930–1935.
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta A, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y . Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 1999; 100: 2473–2476.
Pischon T, Girman CJ, Hotamisligil GS, Rifai N, Hu FB, Rimm EB . Plasma adiponectin levels and risk of myocardial infarction in men. JAMA 2004; 14: 1730–1737.
Spranger J, Kroke A, Möhlig M, Bergmann MM, Ristow M, Boeing H, Pfeiffer AFH . Adiponectin and protection against type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 2003; 361: 226–228.
Maeda N, Takahashi M, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Nishizawa H, Kishida K, Nagaretani H, Matsuda M, Komuro R, Ouchi N, Kuriyama H, Hotta K, Nakamura T, Shimomura I, Matsuzawa Y . PPARy ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes 2001; 50: 2094–2099.
Yang W-S, Jeng C-Y, Wu T-J, Tanaka S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Wang J-P, Chen C-L, Tai T-Y, Chuang L-M . Synthetic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-y agonist, rosiglitazone, increases plasma levels of adiponectin in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 376–380.
Yang W-S, Lee W-J, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Matsuzawa Y, Chao C-L, Chen C-L, Tai T-Y, Chuang L-M . Weight reduction increases plasma levels of an adipose-derived anti-inflammatory protein, adiponectin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 3815–3819.
Faraj M, Havel P, Phelis S, Blank D, Sniderman AD, Cianflone K . Plasma acylation-stimulating protein, adiponectin, leptin, and ghrelin before and after weight loss induced by gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1594–1602.
Yamouchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K, Mori Y, Ide T, Murakami K et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med 2001; 8: 941–946.
Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE . The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med 2001; 8: 947–953.
Engeli S, Feldpausch M, Gorzelniak K, Hartwig F, Heintze U, Janke J, Möhlig M, Pfeiffer AFH, Luft FC, Sharma AM . Association between adiponectin and mediators of inflammation in obese women. Diabetes 2003; 52: 942–947.
Bruun JM, Lihn AS, Verdich C, Pedersen SB, Toubro S, Astrup A, Richelsen B . Regulation of adiponectin by adipose tissue-derived cytokines: in vivo and in vitro investigations in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 285: E527–E533.
Cnop M, Havel PJ, Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Sinha MK, Boyko EJ, Retzlaff BM, Knopp RH, Brunzell JD, Kahn SE . Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia 2003; 46: 459–469.
National Institute of Health. Gastrointestinal Surgery for Severe Obesity: NIH Consensus Development Conference Statement 1991, March 25–27. Am J Clin Nutr 1992; 55: 615S–619S.
Mason E, Doherty C . Vertical banded gastroplasty for morbid obesity. Dig Surg 1997; 14: 355–360.
Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus From the American Diabetes Association, Alexandria, Virginia, Diabetes Care 2002; 25 (Suppl 1): S5–S20.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostatic model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Havel PJ . Update on adipocyte hormones. Regulation of energy balance and carbohydrate/lipid metabolism. Diabetes 2004; 53 (Suppl 1): S143–S151.
Xydakis AM, Case CC, Jones PH, Hoogeveen RC, Liu M-Y, Smith EO, Nelson KW, Ballantyne CM . Adiponectin, inflammation, and the expression of the metabolic syndrome in obese individuals: the impact of rapid weight loss through caloric restriction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 2697–2703.
Lihn AS, Bruun JM, He G, Pedersen SB, Jensen PF, Richelsen B . Lower expression of adiponectin mRNA in visceral adipose tissue in lean and obese subjects. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2004; 1–2: 9–15.
Harris TB, Ferrucci L, Tracy RP, Corti MC, Wacholder S, Ettinger Jr WH, Heimovitz H, Cohen HJ, Wallace R . Association of elevated interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein levels with mortality in the elderly. Am J Med 1999; 106: 506–512.
Ridker PM . High-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Potential adjunct for global risk assessment in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2001; 103: 1813–1818.
Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N . C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 836–843.
Pender C, Goldfine ID, Tanner CJ, Pories WJ, MacDonald KG, Havel PJ, Houmard JA, Youngren JF . Muscle insulin receptor concentrations in obese patients post bariatric surgery: relationship to hyperinsulinemia. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004; 28: 363–369.
Fasshauer M, Kralisch S, Klier M, Lossner U, Bluher M, Klein J, Paschke R . Adiponectin gene expression and secretion is inhibited by interleukin-6 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 4: 1045–1050.
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Nakamura T, Nishida M, Kumada M, Okamoto Y, Ohashi K, Nagaretani H, Kishida K, Nishizawa H, Maeda N, Kobayashi H, Hiraoka H, Matsuzawa Y . Reciprocal Association of c-reactive protein with adiponectin in blood stream and adipose tissue. Circulation 2003; 107: 671–674.
Motoshima H, Wu X, Sinha MK, Hardy VE, Rosato EL, Barbot DJ, Rosato FE, Goldstein BJ . Differential regulation of adiponectin secretion from cultured human omental and subcutaneous adipocytes: effects of insulin and rosiglitazone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 5662–5667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopp, HP., Krzyzanowska, K., Möhlig, M. et al. Effects of marked weight loss on plasma levels of adiponectin, markers of chronic subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance in morbidly obese women. Int J Obes 29, 766–771 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802983
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802983
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of bariatric surgery and dietary intervention on insulin resistance and appetite hormones over a 3 year period
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Change in Adipokines and Gastrointestinal Hormones After Bariatric Surgery: a Meta-analysis
Obesity Surgery (2023)
-
Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on the metabolic profile and systemic inflammatory status of women with metabolic syndrome: randomized controlled clinical trial
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2023)
-
Reasons for discontinuing insulin and factors associated with insulin discontinuation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a real-world evidence study
Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology (2021)
-
Effect of a weight loss program on serum adiponectin and insulin resistance among overweight and obese premenopausal females
Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association (2020)