Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Elevated macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) has been implicated as a causal mechanism in a number of disease conditions including cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, and cancer. Excess body fat is associated with an increased risk of numerous health conditions including CVD, diabetes, and cancer. To our knowledge, the association between MIF and obesity status and the effect of weight loss on serum MIF concentrations have not been reported. In this study, we examined the effects of participation in a behavior-based weight loss program on MIF concentrations in obese individuals.
SUBJECTS:
Study participants were 71 men and women enrolled in The Cooper Institute Weight Management Program. Participants were predominantly female (68%, n=48), middle-aged (46.5±9.8 y), and severely obese (BMI=43.0±8.6).
METHOD:
Plasma MIF concentrations and other standard risk factors were measured before and after participation in a diet and physical activity based weight management program.
RESULTS:
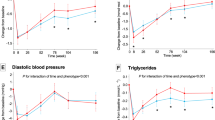
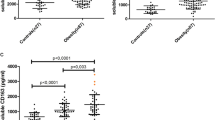
The mean follow-up was 8.5±3.0 months with an average weight loss of 14.4 kg (P<0.001). The majority of clinical risk factors significantly improved at follow-up. Median levels of plasma MIF concentration were significantly lower at follow-up (median [IQR]; 5.1[3.6–10.3]) compared to baseline (8.4 [4.3–48.8]; P=0.0005). The percentage of participants with plasma MIF concentration ≥19.5 mg/nl (highest tertile at baseline) decreased from 33.8 to 5.6% (P<0.001). Further, elevated baseline plasma MIF concentration was associated with markers of β-cell dysfunction and reductions in MIF were associated with improvements in β-cell function.
CONCLUSIONS:
Circulating MIF concentrations are elevated in obese but otherwise healthy individuals; however, this elevation in MIF is not uniform across individuals. In obese individuals with elevated circulating MIF concentrations, participation in physical activity and a dietary-focused weight management program resulted in substantial reduction in MIF.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fingerle-Rowson GR, Bucala R . Neuroendocrine properties of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Immunol Cell Biol 2001; 79/4: 368–375.
Donn RP, Ray DW . Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: molecular, cellular and genetic aspects of a key neuroendocrine molecule. J Endocrinol 2004; 182/1: 1–9.
Pan JH, Sukhova GK, Yang JT, Wang B, Xie T, Fu H, Zhang Y, Satoskar AR, David JR, Metz CN, Bucala R, Fang K, Simon DI, Chapman HA, Libby P, Shi GP . Macrophage migration inhibitory factor deficiency impairs atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Circulation 2004; 109/25: 3149–3153.
Chen Z, Sakuma M, Zago AC, Zhang X, Shi C, Leng L, Mizue Y, Bucala R, Simon D . Evidence for a role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in vascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24/4: 709–714.
Schober A, Bernhagen J, Thiele M, Zeiffer U, Knarren S, Roller M, Bucala R, Weber C . Stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques by blockade of macrophage migration inhibitory factor after vascular injury in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 2004; 109/3: 380–385.
Waeber G, Calandra T, Roduit R, Haefliger JA, Bonny C, Thompson N, Thorens B, Temler E, Meinhardt A, Bacher M, Metz CN, Nicod P, Bucala R . Insulin secretion is regulated by the glucose-dependent production of islet beta cell macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94/9: 4782–4787.
Plaisance V, Thompson N, Niederhauser G, Haefliger JA, Nicod P, Waeber G, Abderrahmani A . The mif gene is transcriptionally regulated by glucose in insulin-secreting cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 295/1: 174–181.
Mitchell RA . Mechanisms and effectors of MIF-dependent promotion of tumourigenesis. Cell Signal 2004; 16/1: 13–19.
Lue H, Kleemann R, Calandra T, Roger T, Bernhagen J . Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): mechanisms of action and role in disease. Microbes Infect 2002; 4/4: 449–460.
Sakaue S, Nishihira J, Hirokawa J, Yoshimura H, Honda T, Aoki K, Tagami S, Kawakami Y . Regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) expression by glucose and insulin in adipocytes in vitro. Mol Med 1999; 5/6: 361–371.
National Institutes of Health and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: The evidence report. National Institutes of Health and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Rockville: MD; pp 1–228; 1998.
Marlatt GA, Gordon JR . Determinants of relapse: implications for the maintenance of behavior change. In: Davidson PO (ed). Behavioral medicine: changing health lifestyles. Pergamon: Elmsford, NY; 1980. pp 410–452.
Isidori AM, Kaltsas GA, Korbonits M, Pyle M, Gueorguiev M, Meinhardt A, Metz C, Petrovsky N, Popovic V, Bucala R, Grossman AB . Response of serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor levels to stimulation or suppression of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in normal subjects and patients with Cushing's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87/4: 1834–1840.
Petrovsky N, Socha L, Silva D, Grossman AB, Metz C, Bucala R . Macrophage migration inhibitory factor exhibits a pronounced circadian rhythm relevant to its role as a glucocorticoid counter-regulator. Immunol Cell Biol 2003; 81/2: 137–143.
Yabunaka N, Nishihira J, Mizue Y, Tsuji M, Kumagai M, Ohtsuka Y, Imamura M, Asaka M . Elevated serum content of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000; 23/2: 256–258.
Vozarova B, Stefan N, Hanson R, Lindsay RS, Bogardus C, Tataranni PA, Metz C, Bucala R . Plasma concentrations of macrophage migration inhibitory factor are elevated in Pima Indians compared to Caucasians and are associated with insulin resistance. Diabetologia 2002; 45/12: 1739–1741.
Benigni F, Atsumi T, Calandra T, Metz C, Echtenacher B, Peng T, Bucala R . The proinflammatory mediator macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces glucose catabolism in muscle. J Clin Invest 2000; 106/10: 1291–1300.
Acknowledgements
We thank our many participants, Abby Hyman for her help with the clinical examinations and data acquisition, Pat McDonald and her staff of the Cooper Clinic, the Management Information Systems division at The Cooper Institute for data entry and management, and Melba Morrow for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Church, T., Willis, M., Priest, E. et al. Obesity, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, and weight loss. Int J Obes 29, 675–681 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802942
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802942
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor polymorphisms are a potential susceptibility marker in systemic sclerosis from southern Mexican population: association with MIF mRNA expression and cytokine profile
Clinical Rheumatology (2019)
-
The macrophage migration inhibitory factor protein superfamily in obesity and wound repair
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2015)
-
Increased activity of interleukin-23/interleukin-17 proinflammatory axis in obese women
International Journal of Obesity (2009)
-
The role of the small intestine in the development of dietary fat-induced obesity and insulin resistance in C57BL/6J mice
BMC Medical Genomics (2008)
-
Effect of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) gene variants and MIF serum concentrations on the risk of type 2 diabetes: results from the MONICA/KORA Augsburg Case–Cohort Study, 1984–2002
Diabetologia (2008)