Abstract
OBJECTIVE: We aimed to study the effect of atorvastatin, a statin, on cholesterol synthesis and absorption and VLDL-apoB metabolism in obese men with the metabolic syndrome.
METHODS: A total of 25 dyslipidaemic obese men were randomized to atorvastatin (n=13) (40 mg/day) or matching placebo (n=12) for 6 weeks. Hepatic secretion and fractional catabolic rate (FCR) of VLDL-apoB was measured using an intravenous bolus of d3-leucine before and after treatment. ApoB isotopic enrichment was measured using GCMS and multicompartmental modelling. Plasma lathosterol: cholesterol and campesterol:cholesterol ratios were determined to assess cholesterol synthesis and cholesterol absorption, respectively.
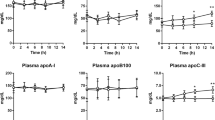
RESULTS: Compared with placebo, atorvastatin significantly decreased (P<0.05) total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-cholesterol and VLDL-apoB. Plasma lathosterol:cholesterol ratio decreased from 26.4±2.4 to 8.8±0.8, while the campesterol:cholesterol ratio increased from 26.5±4.4 to 38.6±5.8 (P<0.01). Atorvastatin also increased VLDL-apoB FCR from 3.82±0.33 to 6.30±0.75 pools/day (P<0.01), but did not significantly alter VLDL-apoB secretion (12.8±1.7 to 13.8±2.0 mg/kg/day).
CONCLUSIONS: In obesity, atorvastatin inhibits cholesterogenesis but increases intestinal cholesterol absorption. The increased cholesterol absorption may counteract the inhibitory effect on hepatic VLDL-apoB secretion, but it does not apparently influence enhanced catabolism of VLDL-apoB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ginsberg HN . Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Invest 2000; 106: 453–458.
Chan DC, Watts GF, Redgrave TG, Mori TA, Barrett PHR . Apolipoprotein B-100 kinetics in visceral obesity: associations with plasma apolipoprotein C-III concentration. Metabolism 2002; 51: 1041–1046.
Thompson GR, Naoumova R, Watts GF . Role of cholesterol in regulating apolipoprotein B secretion by the liver. J Lipid Res 1996; 37: 439–447.
Riches FM, Watts GF, Hua J, Stewart GR, Naoumova RP, Barrett PH . Reduction in visceral adipose tissue is associated with improvement in apolipoprotein B-100 metabolism in obese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84:2854–2861.
Simonen PP, Gylling H, Howard AN, Miettinen TA . Introducing a new component of the metabolic syndrome: low cholesterol absorption. Am J Clin Nutr 2000; 72: 82–88.
Miettinen TA, Tilvis RS, Kesaniemi YA . Serum plant sterols and cholesterol precursors reflect cholesterol absorption and synthesis in volunteers of a randomly selected male population. Am J Epidemiol 1990; 131: 20–31.
Gylling H, Miettinen TA . Effects of inhibiting cholesterol absorption and synthesis on cholesterol and lipoprotein metabolism in hypercholesterolemic non-insulin-dependent diabetic men. J Lipid Res 1996; 37: 1776–1785.
Simonen PP, Gylling H, Miettinen TA . Body weight modulates cholesterol metabolism in non-insulin dependent type 2 diabetics. Obes Res 2002; 10: 328–335.
Watts GF, Naoumova RP, Kelly JM, Riches FM, Croft KD, Thompson GR . Inhibition of cholesterogenesis decreases hepatic secretion of apoB-100 in normolipidemic subjects. Am J Physiol 1997; 273: 462–470.
Watts GF, Cummings MH, Umpleby M, Quiney JR, Naoumova R, Thompson GR . Sonksen PH. Simvastatin decreases the hepatic secretion of very-low-density lipoprotein apolipoprotein B-100 in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. Eur J Clin Invest 1995; 25: 559–567.
Lindenthal B, Sudhop T, Schiedermaier P, Agnan M, Sauerbruch T, von Bergmann K . Serum plant sterols and biliary cholesterol secretion in humans: studies with ursodeoxycholic acid. J Lipid Res 2002; 43: 1072–1077.
Duane WC, Hunninghake DB, Freeman ML, Pooler PA, Schlasner LA, Gebhard RL . Simvastatin, a competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, lowers cholesterol saturation index of gallbladder bile. Hepatology 1988; 8:1147–1150.
Vanhanen H, Kesäniemi YA, Miettinen TA . Pravastatin lowers serum cholesterol, cholesterol-precursor sterols, fecal steroids and cholesterol absorption in man. Metabolism 1992; 41: 588–595.
Duane WC . Effects of lovastatin and dietary cholesterol on sterol homeostasis in healthy human subjects. J Clin Invest 1993; 92: 911–918.
Sehayek E, Ono JG, Shefer S, Nguyen LB, Wang N, Batta AK, Salen G, Smith JD, Tall AR, Breslow JL . Biliary cholesterol excretion: a novel mechanism that regulates dietary cholesterol absorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1998; 95: 10194–10199.
Ostlund RE, Bosner MS, Stenson WF . Cholesterol absorption efficiency declines at moderate dietary doses in normal human subjects. J Lipid Res 1999; 40: 1453–1458.
Kesaniemi YA, Grundy SM . Overproduction of low density lipoproteins associated with coronary heart disease. Arteriosclerosis 1983; 3: 40–46.
Lamarche B, Tchernof A, Mauriege P, Cantin B, Dagenais GR, Lupien PJ, Despres JP . Fasting insulin and apolipoprotein B levels and low-density lipoprotein particle size as risk factors for ischemic heart disease. JAMA 1998; 279: 1955–1961.
Bays HE, Moore PB, Drehobl MA, Rosenblatt S, Toth PD, Dujovne CA, Knopp RH, Lipka LJ, Lebeaut AP, Yang B, Mellars LE, Cuffie-Jackson C, Veltri EP, Ezetimibe Study Group. Effectiveness and tolerability of ezetimibe in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia: pooled analysis of two phase II studies. Clin Ther 2001; 23: 1209–1230.
Berge KE, von Bergmann K, Lutjohann D, Guerra R, Grundy SM, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC . Heritability of plasma noncholesterol sterols and relationship to DNA sequence polymorphism in ABCG5 and ABCG8. J Lipid Res 2002 43: 486–494.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Heart Foundation of Australia, the National Health Medical Research Council of Australia, the Medical Research Foundation (Royal Perth Hospital), Pfizer Australia and the National Institutes of Health (NCRR 12609). PHRB is a Career Development Fellow of the National Heart Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watts, G., Chan, D., Barrett, P. et al. Effect of a statin on hepatic apolipoprotein B-100 secretion and plasma campesterol levels in the metabolic syndrome. Int J Obes 27, 862–865 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802287
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802287
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A whole-body mathematical model of cholesterol metabolism and its age-associated dysregulation
BMC Systems Biology (2012)
-
Probucol Suppresses Enterocytic Accumulation of Amyloid‐β Induced by Saturated Fat and Cholesterol Feeding
Lipids (2012)
-
Messenger RNA levels of genes involved in dysregulation of postprandial lipoproteins in type 2 diabetes: the role of Niemann–Pick C1-like 1, ATP-binding cassette, transporters G5 and G8, and of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein
Diabetologia (2006)
-
I costi della sindrome metabolica
PharmacoEconomics Italian Research Articles (2005)