Abstract
Objective: To investigate the independent influence of alterations in fat mass, body fat distribution and hormone release on pubertal increases in fasting serum insulin concentrations and on insulin resistance assessed by the homeostasis model (HOMA).
Design and Subjects: Cross-sectional investigation of pre- (n=11, n=8), mid- (n=10, n=11), and late-pubertal (n=10, n=11) boys and girls with normal body weight and growth velocity.
Measurements: Body composition (by a four-compartment model), abdominal fat distribution and mid-thigh interfascicular plus intermuscle (extramyocellular) fat (by magnetic resonance imaging), total body subcutaneous fat (by skinfolds), mean nocturnal growth hormone (GH) release and 06:00 h samples of serum insulin, sex steroids, leptin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I).
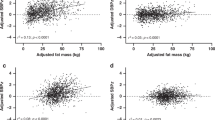
Results: Pubertal insulin resistance was suggested by greater (P<0.001) fasting serum insulin concentrations in the late-pubertal than pre- and mid-pubertal groups while serum glucose concentrations were unchanged and greater (P<0.001) HOMA values in late-pubertal than pre- and mid-pubertal youth. From univariate correlation fat mass was most related to HOMA (r=0.59, P<0.001). Two hierarchical regression models were developed to predict HOMA. In one approach, subject differences in sex, pubertal maturation, height and weight were held constant by adding these variables as a block in the first step of the model (r2=0.36). Sequential addition of fat mass (FM) increased r2 (r2(inc)remental=0.08, r2=0.44, P<0.05) as did the subsequent addition of a block of fat distribution variables (extramyocellular fat, abdominal visceral fat, and sum of skinfolds; r2inc=0.11, r2=0.55, P<0.05). Sequential addition of a block of hormone variables (serum IGF-I and log(10) leptin concentrations; r2inc=0.04, P>0.05) did not reliably improve r2 beyond the physical characteristic and adiposity variables. In a second model, differences in sex and pubertal maturation were again held constant (r2=0.25), but body size differences were accounted for using percentage fat data. Sequential addition of percentage body fat (r2(inc)remental=0.11, r2=0.36, P<0.05), then a block of fat distribution variables (percentage extramyocellular fat, percentage abdominal visceral fat, and percentage abdominal subcutaneous fat; r2inc=0.08, r2=0.44, P=0.058), and then a block of serum IGF-I and log(10) leptin concentrations (r2inc=0.07, r2=0.51, P<0.05) increased r2. Mean nocturnal GH release was not related to HOMA (r=−0.04, P=0.75) and therefore was not included in the hierarchical regression models.
Conclusion: Increases in insulin resistance at puberty were most related to FM. Accumulation of fat in the abdominal visceral, subcutaneous and muscular compartments may increase insulin resistance at puberty beyond that due to total body fat. Serum concentrations of leptin and IGF-I may further modulate HOMA beyond the effects of adiposity and fat distribution. However, the results are limited by the cross-sectional design and the use of HOMA rather than a criterion measure of insulin resistance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloch CA, Clemons P, Sperling MA . Puberty decreases insulin sensitivity J Pediatr 1987 110: 481–487.
Moran A, Jacobs DR, Steinberger J, Hong C-P, Prineas R, Luepker R, Sinaiko AR . Insulin resistance during puberty. Results from clamp studies in 357 children Diabetes 1999 48: 2039–2044.
Potau N, Ibanez L, Rique S, Carrascosa A . Pubertal changes in insulin secretion and peripheral insulin sensitivity Horm Res 1997 48: 219–226.
Caprio S, Plewe G, Diamond MP, Simonson DC, Boulware SD, Sherwin RS, Tamborlane WV . Increased insulin secretion in puberty: a compensatory response to reductions in insulin sensitivity J Pediatr 1989 114: 963–967.
Dietz WH . Critical periods in childhood for the development of obesity Am J Clin Nutr 1994 59: 955–959.
Amiel SA, Caprio S, Sherwin RS, Plewe G, Haymond MW, Tamborlane WV . Insulin resistance of puberty: a defect restricted to peripheral glucose metabolism J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991 72: 277–282.
Caprio S, Hyman LD, Limb C, McCarthy S, Lange R, Sherwin RS, Shulman G, Tamborlane WV . Central adiposity and its metabolic correlates in obese adolescent girls Am J Physiol 1995 269: E118–E126.
Caprio S, Hyman LD, McCarthy S, Lange R, Bronson M, Tamborlane WV . Fat distribution and cardiovascular risk factors in obese adolescent girls: importance of the intrabdominal fat depot Am J Clin Nutr 1996 64: 12–17.
Caprio S, Tamborlane WV, Silver D, Robinson C, Leibel R, McCarthy S, Grozman A, Belous A, Maggs D, Sherwin RS . Hyperleptinemia: an early sign of juvenile obesity. Relations to body fat depots and insulin concentrations Am J Physiol 1996 271: E626–E630.
Brambilla P, Manzoni P, Sironi S, Simone P, Del Maschio A, di Natale B, Chiumello G . Peripheral and abdominal adiposity in childhood obesity Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1994 18: 795–800.
Goodpaster BH, Thaete FL, Simoneau JA, Kelley DE . Subcutaneous abdominal fat and thigh muscle composition predict insulin sensitivity independently of visceral fat Diabetes 1997 46: 1579–1585.
Abate N, Garg A, Peshock RM, Stray-Gundersen J, Grundy S . Relationships of generalized and regional adiposity to insulin sensitivity in men J Clin Invest 1995 96: 88–98.
Pan DA, Lillioja S, Kriketos AD, Milner MR, Baur LA, Bogardus C, Jenkins AB, Storlein LH . Skeletal muscle triglyceride levels are inversely related to insulin action Diabetes 1997 46: 983–988.
Phillips DIW, Caddy S, Ilic V, Fielding BA, Frayn KN, Borthwick AC, Taylor R . Muscle triglyceride and muscle insulin sensitivity: evidence for a relationship in nondiabetic subjects Metabolism 1996 45: 947–950.
Simoneau JA, Colberg SR, Thaete FL, Kelley DE . Skeletal muscle glycolytic and oxidative enzyme capacities are determinants of insulin sensitivity and muscle composition in obese women FASEB J 1995 9: 273–278.
Storlien LH, Jenkins AB, Chrisholm DJ, Pascoe WS, Khouri S, Kraegen EW . Influence of dietary fat composition on development of insulin resistance in rats. Relationship to muscle triglyceride and −3 fatty acids in muscle phospholipid Diabetes 1991 40: 280–289.
Caprio S, Bronson M, Sherwin RS, Rife F, Tamborlane WV . Co-existence of severe insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in pre-adolescent obese children Diabtologia 1996 39: 1489–1497.
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R . Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance Am J Physiol 1979 237: E214–E233.
Shulman GI, Rothman DL, Jue T, Stein P, DeFronzo RA, Shulman RG . Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy New Engl J Med 1990 322: 223–228.
Fehmann H-C, Berghofer P, Brandhorst D, Brandhorst H, Hering B, Bretzel RG, Goke B . Leptin inhibition of insulin secretion from isolated human islets Acta Diabetol 1997 34: 249–252.
Roemmich JN, Clark PA, Berr S, Mai V, Mantzoros C, Weltman A, Flier JS, Rogol AD . Gender differences in leptin levels during puberty are related to the subcutaneous fat depot and sex steroids Am J Physiol 1998 275: E543–E551.
Bareille P, Azcona C, Matthews DR, Conway GS, Stanhope R . Lipid profile, glucose tolerance, and insulin sensitivity after more than four years of growth hormone therapy in non-growth hormone deficient adolescents Clin Endocrinol 1999 51: 347–353.
Amiel SA, Sherwin RS, Simonson DC, Lauritano AA, Tamborlane WV . Impaired insulin action in puberty New Engl J Med 1986 315: 215–219.
Cook JS, Hoffman RP, Stene MA, Hansen JR . Effects of maturational stage on insulin sensitivity during puberty J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993 77: 725–730.
Caprio S . Insulin: the other anabolic hormone of puberty Acta Paediatr 1999 433 (Suppl): 84–87.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man Diabetologia 1985 28: 412–419.
Tanner JM . Growth at adolescence Blackwell Scientific: Oxford 1962.
Roemmich JN, Clark PA, Mai V, Berr S, Weltman A, Veldhuis JD, Rogol AD . Alterations in growth and body composition during puberty: III. Influence of maturation, gender, body composition, fat distribution, aerobic fitness, and energy expenditure on nocturnal growth hormone release during puberty J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998 83: 1440–1447.
Veldhuis JD, Johnson ML . Cluster analysis: a simple, versatile, and robust algorithm for endocrine detection Am J Physiol 1986 250: E486–E493.
Lohman TG . Advances in body composition assessment Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL 1992.
Roemmich JN, Clark PA, Weltman A, Rogol AD . Alterations in growth and body composition during puberty: I. Comparison among 2-, 3- and 4-compartment models of body composition J Appl Physiol 1997 83: 927–935.
Harrison GG, Buskirk ER, Lindsay Carter JE, Johnston FE, Lohman TG, Pollack ML, Roche AF, Wilmore JH . 1988 Skinfold thicknesses and measurement technique. In: Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R (eds) Anthropometric standardization reference manual Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL 1988 55–70.
Radziuk J . Insulin sensitivity and its measurement: structural commonalities among the methods J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000 85: 4426–4433.
Petrie JR, Morris AD, Dorrian CA, Small M, Connell JM . Specific insulin assays, insulin sensitivity and blood pressure Q J Med 1997 90: 465–475.
Gower BA, Nagy TR, Goran MI . Visceral fat, insulin sensitivity, and lipids in prepubertal children Diabetes 1999 48: 1515–1521.
Arslanian S, Suprasongsin C . Insulin sensitivity, lipids, and body composition in childhood: is ‘syndrome X’ present? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996 81: 1058–1062.
Jiang X, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS . Relation of obesity to insulin secretion and clearance in adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996 20: 951–956.
Radetti G, Ghizzoni L, Paganini C, Iughetti L, Caselli G, Bernasconi S . Insulin pulsatility in obese and normal prepubertal children Horm Res 1998 50: 78–82.
Smith CP, Dunger DB, Williams AJK, Taylor AM, Perry LA, Gale EAM, Preece MA, Savage MO . Relationship between insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate concentrations during childhood, puberty, and adult life J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1989 68: 932–937.
Pouliot M-C, Despres J-P, Lemieux S, Moorjani S, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Lupien PJ . Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women Am J Cardiol 1994 73: 460–468.
Gower BA, Nagy TR, Trowbridge CA, Dezenberg C, Goran MI . Fat distribution and insulin response in prepubertal African American and white children Am J Clin Nutr 1998 67: 821–827.
Boden G, Lebed B, Schatz M, Homko C, Lemieu S . Effects of acute changes of plasma free fatty acids on intramyocellular fat content and insulin resistance of healthy subjects Diabetes 2001 50: 1612–1617.
Perseghin G, Scifo P, De Cobelli F, Pagliato E, Battezzati A, Arcelloni C, Vanzulli A, Testolin G, Pozza G, Del Maschio A, Luzi L . Intramyocellular triglyceride content is a determinant of in vivo insulin resistance in humans: a 1H–13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy assessment in offspring of type 2 diabetic parents Diabetes 2001 48: 1600–1606.
Arslanian SA, Heil BV, Becker DJ, Drash AL . Sexual dimorphism in insulin sensitivity in adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991 72: 920–926.
Heptulla RA, Boulware SD, Caprio S, Silver D, Sherwin RS, Tamborlane WV . Decreased insulin sensitivity and compensatory hyperinsulinemia after hormone treatment in children with short stature J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 3234–3238.
Seminara S, Merello G, Masi S, Filpo A, La Cauza F, D'Onghia G, Martelli E, Loche S . Effect of long-term growth hormone treatment on carbohydrate metabolism in children with growth hormone deficiency Clin Endocrinol 1998 49: 125–130.
Travers SH, Jeffers BW, Blocj CA, Hill JO, Eckel RH . Gender and Tanner stage differences in body composition and insulin sensitivity in early pubertal children J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995 80: 172–178.
Clemmons DR, Moses AC, McKay MJ, Sommer A, Rosen DM, Ruckle J . The combination of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 reduces insulin requirements in insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes: evidence of in vivo biological activity J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000 85: 1518–1524.
Schwartz MW, Baskin DG, Kaiyala KJ, Woods SC . Model for the regulation of energy balance and adiposity by the central nervous system Am J Clin Nutr 1999 69: 584–596.
Emilsson V, Liu YL, Cawthorne MA, Morton NM, Davenport M . Expression of the functional leptin receptor mRNA in pancreatic islets and direct inhibitory action of leptin on insulin secretion Diabetes 1997 46: 313–316.
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Ms Sandra Jackson and the nursing staff at the University of Virginia General Clinical Research Center who provided patient care and Katy Nash, MS and Catherine DeGood for study coordination. We thank Bret Goodpaster PhD for his insightful suggestions on an earlier version of this paper. We acknowledge the subjects for their enthusiasm for the research program. This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health HD 32631 (ADR), General Clinical Research Center grants MO1 RR00847 (University of Virginia), the Genentech Foundation for Growth and Development (PAC), and the University of Virginia Children's Medical Center (JNR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roemmich, J., Clark, P., Lusk, M. et al. Pubertal alterations in growth and body composition. VI. Pubertal insulin resistance: relation to adiposity, body fat distribution and hormone release. Int J Obes 26, 701–709 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801975
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801975
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Trends in HOMA-IR values among South Korean adolescents from 2007–2010 to 2019–2020: a sex-, age-, and weight status-specific analysis
International Journal of Obesity (2023)
-
Body composition and insulin resistance in children
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2018)
-
Insulin Resistance of Puberty
Current Diabetes Reports (2016)
-
Elevated blood pressure in adolescent girls: correlation to body size and composition
BMC Public Health (2015)
-
Inverse correlation of serum inflammatory markers with metabolic parameters in healthy, Black and White prepubertal youth
International Journal of Obesity (2014)