Abstract
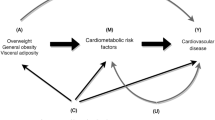
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the inter-relationships of age- and menopause- related changes of general obesity and body fat distribution and their independent effects on cardiovascular risk factors.
DESIGN: Cross-sectional study.
SUBJECTS: One-hundred and thirty-six premenopausal and 193 postmenopausal Chinese women with body mass index (BMI)<30 kg/m2.
MEASUREMENTS: Anthropometric surrogates of general obesity (BMI, total body fat percentage) and central obesity (waist-to-hip ratio, centrality index) were measured. Blood pressure, 75 g oral glucose tolerance test, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c and lipid profiles were also measured.
RESULTS: Significant correlation coefficients between age, general obesity, central obesity and cardiovascular disease risk factors were noted. Through the menopausal transition, the BMI and total body fat percentage were increased significantly. After adjustments for age and BMI, the postmenopausal women showed higher android fat percentage, centrality index, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c, serum concentrations of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and atherogenic indices than the premenopausal women. In multiple stepwise regression models, age exerted independent effects on oral glucose tolerance test 2 h plasma glucose level, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol level, and LDL cholesterol. Menopause was an independent variable in relation to the changes of glycosylated hemoglobin A1c, total and LDL cholesterol levels, triglyceride levels and atherogenic indices. The centrality index was the major independent variable of all the cardiovascular disease risk factors, except total and LDL cholesterol level. However, the variation of total body fat percentage had no independent effect on any cardiovascular disease risk factors.
CONCLUSION: Through the aging and menopausal effects, women will increase total body fat content, favoring the central body fat distribution. Age, menopause and central obesity were all independent and significant factors to the cardiovascular disease risk factors in Chinese women.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lerner DJ, Kannel WB . Patterns of coronary heart disease morbidity and mortality in the sexes: a 26-year follow-up of the Framingham population Am Heart J 1986 111: 383–390.
Skafar DF, Xu R, Morales J, Ram J, Sowers JR . Female sex hormones and cardiovascular disease in women J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 3913–3918.
Barret-Corner E, Bush TL . Estrogen and coronary heart disease in women JAMA 1991 265: 1861–1867.
Going S, Williams D, Lohman T . Aging and body composition: biological changes and methodological issues Exerc Sport Sci Rev 1995 23: 411–458.
Poehlman ET, Toth MJ, Gardner AW . Changes in energy balance and body composition at menopause: a controlled longitudinal study Ann Intern Med 1995 123: 673–675.
Heymsfield SB, Gallagher D, Poehlman ET, Wolper C, Nonas K, Selson D, Wang ZM . Menopausal changes in body composition and energy expenditure Exp Gerontol 1994 29: 377–389.
Pedersen SB, Børglum JD, Brixen K, Richelsen B . Relationship between sex hormones, body composition and metabolic risk parameters in premenopausal women Eur J Endocrinol 1995 133: 200–206.
Svendsen OL, Hassager C, Christiansen C . Relationships and independence of body composition, sex hormones, fat distribution and other cardiovascular risk factors in overweight postmenopausal women Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1993 17: 459–463.
Larsson B, Bengtsson C, Björntorp P, Lapidus L, Sjöström L, Svådsudd K, Tibblin G, Wedel H, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L . Is abdominal body fat distribution a major explanation for the sex difference in the incidence of myocardial infarction? Am J Epidemiol 1992 135: 266–273.
Freedman DS, Jacobsen SJ, Barboriak JJ, Sobocinski K, Anderson AJ, Kissebah AH, Sasse EA, Gruchow HW . Body fat distribution and male/female differences in lipids and lipoproteins Circulation 1990 81: 1498–1506.
Tchernof A, Poehlman ET . Effects of the menopause transition on body fatness and body fat distribution Obes Res 1998 6: 246–254.
Troisi RJ, Wolf AM, Mason JE, Klingler KM, Colditz GA . Relation of body fat distribution to reproductive factors in pre and postmenopausal women Obes Res 1995 3: 143–151.
Pasquali R, Vicennati V, Bertazzo D, Casimirri F, Pascal G, Tortelli O, Morselli Labate AM . Determinants of sex hormone-binding globulin blood concentrations in premenopausal and postmenopausal women with different estrogen status Metabolism 1997 46: 5–9.
Bjorkelund C, Lissner L, Andresson S, Lapidus L, Bengtsson C . Reproductive history in relation to relative weight and fat distribution Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996 20: 213–219.
Tremollieres FA, Pouilles JM, Ribot CA . Relative influence of age and menopause on total and regional body composition changes in postmenopausal women Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996 175: 1594–1600.
Kirchengast S, Gruber D, Sator M, Hartmann B, Knogler W, Huber J . Menopause-associated differences in female fat patterning estimated by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry Ann Hum Biol 1997 24: 45–54.
Svendsen OL, Hassager C, Christiansen C . Age- and menopause-associated variations in body composition and fat distribution in healthy women as measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry Metabolism 1995 44: 369–373.
Poehlman ET, Toth MJ, Ades PA, Rosen CJ . Menopause-associated changes in plasma lipids, insulin-like growth factor 1 and blood pressure: a longitudinal study Eur J Clin Invest 1997 27: 322–326.
Wang Q, Hassager C, Ravn P, Wang S, Christiansen C . Total and regional body-composition changes in early postmenopausal women: age-related or menopause-related? Am J Clin Nutr 1994 60: 843–848.
Chang CJ, Wu CH, Lu FH, Wu JS, Chiu NT, Yao WJ . Discriminating glucose tolerance status by ROIs of DEXA: clinical implications of body fat distribution Diabetes Care 1999 22: 1938–1943.
Pasquali R, Casimirri F, Pascal G, Tortelli O, Morselli Labate AM, Bertazzo D, Vicennati V, Gaddi A . Influence of menopause on blood cholesterol levels in women: the role of body composition, fat distribution and hormonal milieu J Intern Med 1997 241: 195–203.
Williams MJ, Hunter GR, Kekes-Szabo T, Snyder S, Treuth MS . Regional fat distribution in women and risk of cardiovascular disease Am J Clin Nutr 1997 65: 855–860.
International Obesity Task Force . Global prevalence and secular trends in obesity. In Obesity:preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of WHO Consultation on Obesity, Geneva, 3–5 June 1997 World Health Organization: Geneva.
Samaras K, Kelly PJ, Spector TD, Chiano MN, Campbell LV . Tobacco smoking and oestrogen replacement are associated with lower total and central fat in monozygotic twins Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 149–156.
Samaras K, Spector TD, Nguyen TV, Baan K, Campbell LV, Kelly PJ . Independent genetic factors determine the amount and distribution of fat in women after the menopause J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 781–785.
Seidell JC, Cigolini M, Charzewska J, Ellsinger BM, Di Biase G . Fat distribution in European women: a comparison of anthropometric measurements in relation to cardiovascular risk factors Int J Epidemiol 1990 19: 303–308.
Ley CJ, Lees B, Stevenson JC . Sex- and menopause-associated changes in body-fat distribution Am J Clin Nutr 1992 55: 950–954.
Walton C, Lees B, Crook D, Godsland IF, Stevenson JC . Relationships between insulin metabolism, serum lipid profile, body fat distribution and blood pressure in healthy men Atherosclerosis 1995 118: 35–43.
Frohlich ED, Grim C, Labarthe DR, Maxwell MH, Perloff D, Weidman WH . Recommendation for human blood pressure determination by sphygmomanometers. Report of a task force appointed by the Steering Committee, American Heart Association Hypertension 1988 11: 209A–222A.
Haarbo J, Marslew U, Gotfredsen A, Christiansen C . Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy prevents central distribution of body fat after menopause Metabolism 1991 40: 1323–1326.
Hunter GR, Kekes-Szabo T, Treuth MS, Williams MJ, Goran M, Pichon C . Intra-abdominal adipose tissue, physical activity and cardiovascular risk in pre- and post-menopausal women Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996 20: 860–865.
Bonora E, del Prato S, Bonadonna RC, Gulli G, Solini A, Shank ML, Ghiatas AA, Lancaster JL, Kilcoyne RF, Alyassin AM, DeFronzo RA . Total body fat content and fat topography are associated differently with in vivo glucose metabolism in nonobese and obese nondiabetic women Diabetes 1992 41: 1151–1159.
Carey DG, Jenkins AB, Campbell LV, Freund J, Chisholm DJ . Abdominal fat and insulin resistance in normal and overweight women Diabetes 1996 45: 633–638.
Schlesselman JJ . Case Control Studies: Design, Conduct, Analysis Oxford University Press: New York 1982.
Björntorp P . The regulation of adipose tissue distribution in humans Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996 20: 291–302.
Rebuffé-Scrive M, Enk L, Crona N, Lönnroth P, Abrahamsson L, Smioth U, Björntorp P . Fat cell metabolism in different regions in women J Clin Invest 1985 75: 1973–1976.
Rebuffé-Scrive M, Lönnroth P, Mårin P, Wesslau C, Björntorp P, Smith U . Regional adipose tissue metabolism in men and postmenopausal women Int J Obes 1987 11: 347–355.
Svendsen OL, Hassager C, Christiansen C . Impact of regional and total body composition and hormones on resting energy expenditure in overweight postmenopausal women Metabolism 1993 42: 1588–1591.
Wells CL, Boorman MA, Riggs DM . Effects of age and menopausal status on cardiorespiratory fitness in masters women runners Med Sci Sports Exerc 1992 24: 1147–1154.
Carey DGP, Nguyen TV, Campbell LV, Chisholm DJ, Kelly P . Genetic influences on central abdominal fat: a twin study Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996 20: 722–726.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grant NCKUH 88-051. We wish to thank Ma Mi-Chia, PhD, Associate Professor in the Department of Statistics of National Cheng Kung University, for her statistical assistance. We would also like to thank Mr Chen Eng-Jun for his technical assistance on DEXA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, CJ., Wu, CH., Yao, WJ. et al. Relationships of age, menopause and central obesity on cardiovascular disease risk factors in Chinese women. Int J Obes 24, 1699–1704 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801457
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801457
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A review of menopause nomenclature
Reproductive Health (2022)
-
Prevalence and risk factors of type 2 diabetes in middle-aged women in Northern Vietnam
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries (2016)
-
Large artery stiffness and carotid intima-media thickness in relation to markers of calcium and bone mineral metabolism in African women older than 46 years
Journal of Human Hypertension (2015)
-
Changes in body fat distribution through menopause increase blood pressure independently of total body fat in middle-aged women: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2010
Hypertension Research (2013)
-
Survival benefit of abdominal adiposity: a 6-year follow-up study with Dual X-ray absorptiometry in 3,978 older adults
AGE (2012)