Abstract
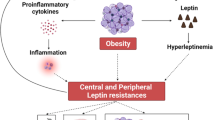
OBJECTIVE: Leptin, the ob gene product, is an anorexigenic peptide secreted from adipose tissue. However, the mechanism of leptin clearance/degradation has not been well determined in humans. The present study was undertaken to examine a possible involvement of liver in determining circulating leptin concentrations in humans.
SUBJECTS: In the present study 58 healthy control subjects and 68 patients with liver cirrhosis (LC) without any renal dysfunction were randomly included.
METHOD: The serum immunoreactive leptin (IRL) concentrations relative to the body mass index (BMI) were determined. Serum IRL and estradiol (E2) concentrations were assayed by radioimmunoassay (RIA).
RESULTS: The correlations between the BMI and circulating IRL concentrations were all significant in male healthy controls (M-C), male patients with LC (M-LC), female healthy controls (F-C) and female patients with LC (F-LC). Circulating IRL concentrations were significantly higher than control in F-LC but not M-LC groups. The ratio of circulating IRL concentrations to the BMI was significantly higher in the M-LC group than in the M-C group and also significantly higher in the F-LC group than in the F-C group. The correlation between the IRL/BMI ratio and serum total bilirubin concentrations was significant (r=0.417, P<0.05) in the M-LC group, but not in the F-LC group. There was no significant correlation of the IRL/BMI ratio to serum E2 or albumin concentrations in either M-LC or F-LC groups.
CONCLUSION: The present data demonstrated that the rate of increase in circulating IRL concentrations with the BMI was higher in LC patients of both genders. Liver may play a role in determining circulating leptin levels.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimizu, H., Kakizaki, S., Tsuchiya, T. et al. An increase of circulating leptin in patients with liver cirrhosis. Int J Obes 22, 1234–1238 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800768
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800768
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Serum leptin levels in alcoholic liver cirrhosis: relationship with gender, nutritional status, liver function and energy metabolism
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2001)
-
Relative hypoleptinemia in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus
International Journal of Obesity (2000)