Abstract
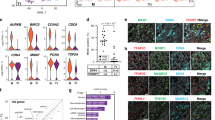
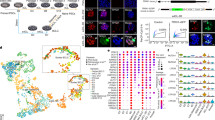
Epigenetic reprogramming resets parental epigenetic memories and differentiates primordial germ cells (PGCs) into mitotic pro-spermatogonia or oogonia, ensuring sexually dimorphic germ-cell development for totipotency 1. In vitro reconstitution of epigenetic reprogramming in humans remains a fundamental challenge. Here, we establish a robust strategy for inducing epigenetic reprogramming and differentiation of pluripotent stem cell (PSC)-derived human PGC-like cells (hPGCLCs) into mitotic pro-spermatogonia or oogonia, coupled with their extensive amplification (~>1010-fold). Strikingly, bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signalling is a key driver of these processes: BMP-driven hPGCLC differentiation involves an attenuation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) pathway and both de novo and maintenance DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) activities, likely promoting replication-coupled, passive DNA demethylation. On the other hand, hPGCLCs deficient in tens-eleven translocation (TET) 1, an active DNA demethylase abundant in human germ cells 2,3, differentiate into extraembryonic cells, including amnion, with de-repression of key genes bearing bivalent promoters; these cells fail to fully activate genes vital for spermatogenesis and oogenesis, with their promoters remaining methylated. Our study elucidates the framework of epigenetic reprogramming in humans, making a fundamental advance in human biology, and through the generation of abundant mitotic pro-spermatogonia and oogonia-like cells, represents a milestone for human in vitro gametogenesis (IVG) research and its potential translation into reproductive medicine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-3 and Supplementary Discussions 1&2.
Supplementary Tables
This folder contains Supplementary Tables 1-12.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murase, Y., Yokogawa, R., Yabuta, Y. et al. In vitro reconstitution of epigenetic reprogramming in the human germ line. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07526-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07526-6
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.