Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Animal cryptochromes mediate magnetoreception by an unconventional photochemical mechanism
Animal cryptochromes mediate magnetoreception by an unconventional photochemical mechanism
Animals use the Earth's magnetic field for orientation but the biophysical basis of this is unclear. The light-dependent magnetic sense of Drosophila melanogaster was recently shown to be mediated by the cryptochrome (Cry) photoreceptor; here, using a transgenic approach, the type 1 and 2 Cry of the monarch butterfly are shown to both function in the magnetoreception system of Drosophila, and probably use an unconventional photochemical mechanism.
- Robert J. Gegear
- , Lauren E. Foley
- & Steven M. Reppert
-
Letter |
 Genome-wide erasure of DNA methylation in mouse primordial germ cells is affected by AID deficiency
Genome-wide erasure of DNA methylation in mouse primordial germ cells is affected by AID deficiency
The extent of epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian primordial germ cells (PGCs) and in early embryos, and its molecular mechanisms, are poorly understood. DNA methylation profiling in PGCs now reveals a genome–wide erasure of methylation, with female PGCs being less methylated than male ones. A deficiency of the cytidine deaminase AID interferes with the genome–wide erasure of DNA methylation, indicating that AID has a critical function in epigenetic reprogramming.
- Christian Popp
- , Wendy Dean
- & Wolf Reik
-
News |
 Virus spreads by bouncing off infected cells
Virus spreads by bouncing off infected cells
Viral ping-pong lets vaccinia get to other cells faster.
- Brian Vastag
-
News |
 Superbug family tree sketched out
Superbug family tree sketched out
Next-generation genome sequencing enables detailed tracking of MRSA infections.
- Lucas Laursen
-
Research Highlights |
 Evolutionary biology: Sperm signals
Evolutionary biology: Sperm signals
-
-
Research Highlights |
Biochemistry: Designer label
-
Research Highlights |
Neuropharmacology: Beating depression
-
News |
 GlaxoSmithKline goes public with malaria data
GlaxoSmithKline goes public with malaria data
Company to place structures and properties of drug leads in the public domain.
- Declan Butler
-
News |
 Genomics boosts brain-cancer work
Genomics boosts brain-cancer work
Molecular findings start to open up avenues of diagnosis and treatment.
- Erika Check Hayden
-
Books & Arts |
 Vision of a personal genomics future
Vision of a personal genomics future
The director of the US National Institutes of Health, Francis Collins, calls for a revolution in personalized medicine. Such advances should be shared beyond the developed world, says Abdallah S. Daar.
- Abdallah S. Daar
-
News |
 Brother sperm train together
Brother sperm train together
Mouse sperm cells team up with their kin in the race to fertilize eggs.
- John Whitfield
-
Column |
 World view: Wild goose chase
World view: Wild goose chase
Quantitative research assessment is a bad idea whose time has come, argues Colin Macilwain.
- Colin Macilwain
-
Letter |
 Competition drives cooperation among closely related sperm of deer mice
Competition drives cooperation among closely related sperm of deer mice
Sperm can increase their swimming velocity and gain a competitive advantage over sperm from another male by forming cooperative groups, such that selection should favour cooperation of the most closely related sperm. Sperm of deer mice are now shown to aggregate more often with conspecific than heterospecific sperm, in accordance with this theory, whereas in a monogamous species lacking sperm competition, sperm indiscriminately group with unrelated conspecific sperm.
- Heidi S. Fisher
- & Hopi E. Hoekstra
-
News |
 Geologists to evaluate future Haiti risks
Geologists to evaluate future Haiti risks
Hunt for survey markers may reveal crucial data.
- Rex Dalton
-
Letter |
 Genome-wide RNAi screen identifies human host factors crucial for influenza virus replication
Genome-wide RNAi screen identifies human host factors crucial for influenza virus replication
High mutation rates in the influenza A virus facilitate the generation of viral escape mutants, rendering vaccines and drugs potentially ineffective, but targeting host cell determinants could prevent viral escape. Here, 287 human host cell genes influencing influenza A virus replication are found using a genome-wide RNA interference screen. An independent assay is then used to investigate overlap between genes necessary for different viral strains.
- Alexander Karlas
- , Nikolaus Machuy
- & Thomas F. Meyer
-
News |
 Israel hails first steps towards funding agency
Israel hails first steps towards funding agency
Weightier grants will provide security for biomedical researchers.
- Haim Watzman
-
Editorial |
Lessons from a pandemic
It is time to assess what worked, and what didn't, in the global efforts to cope with swine flu.
-
-
Research Highlights |
Neuroscience: Dark migraine relief
-
-
Research Highlights |
Immunology: Double punch for HIV
-
News Feature |
 Neuroscience: The most vulnerable brains
Neuroscience: The most vulnerable brains
An increase in premature births means that more babies are at risk of neurological damage. Erika Check Hayden talks with researchers who are developing ways to help these children.
- Erika Check Hayden
-
Editorial |
Call for a bigger vision
Science in Canada cannot realize its full potential without clear direction from government.
-
Opinion |
 Canada needs a polar policy
Canada needs a polar policy
A lack of coordination in Arctic research funding leaves scientists without the support they need for fieldwork. John England outlines how Canada can set things right, and show leadership in the north.
- John England
-
News Feature |
 Swine flu: Crisis communicator
Swine flu: Crisis communicator
Richard Besser led the United States' top public-health agency as swine flu broke out on its doorstep. And his communication shaped the early days of a pandemic, finds Brendan Maher.
- Brendan Maher
-
News |
 Streamlined chemical tests rebuffed
Streamlined chemical tests rebuffed
Europe impedes introduction of REACH safety assessments.
- Natasha Gilbert
-
Letter |
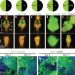 Interaction between RasV12 and scribbled clones induces tumour growth and invasion
Interaction between RasV12 and scribbled clones induces tumour growth and invasion
In human tumours, complex cell interactions in the tumour and its microenvironment are thought to have an important role in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. In a genetically well-defined model system in Drosophila, clones of cells bearing different mutations are now shown to cooperate to promote tumour growth and invasion. This interaction involves JNK signalling propagation and JNK-induced upregulation of JAK/STAT-activating cytokines.
- Ming Wu
- , José Carlos Pastor-Pareja
- & Tian Xu
-
Article |
 Targeting Bcr–Abl by combining allosteric with ATP-binding-site inhibitors
Targeting Bcr–Abl by combining allosteric with ATP-binding-site inhibitors
GNF-2 is a recently discovered, selective allosteric Bcr–Abl inhibitor. Solution NMR, X-ray crystallography, mutagenesis and hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry are now used to show that GNF-2 binds to the myristate-binding site of Abl, leading to changes in the structural dynamics of the ATP-binding site. The results show that the combination of allosteric and ATP-competitive inhibitors can overcome resistance to either agent alone.
- Jianming Zhang
- , Francisco J. Adrián
- & Nathanael S. Gray
-
News |
 Bisphenol A link to heart disease confirmed
Bisphenol A link to heart disease confirmed
Second study supports an association between the controversial chemical and cardiovascular problems.
- Brendan Borrell
-
News |
 Driveways could spread toxins into the home
Driveways could spread toxins into the home
Carcinogens in coal tar–sealed pavements cause worry.
- Nicola Jones
-
Letter |
 Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
The role of B-cell-receptor (BCR) signalling in human B cell lymphomas has been a long-standing question, with genetic and functional evidence for its oncogenic role in human lymphomas lacking. Here, a form of 'chronic active' BCR signalling that is required for cell survival in the activated B-cell-like subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is described and analysed, with potential implications for future therapeutic strategies.
- R. Eric Davis
- , Vu N. Ngo
- & Louis M. Staudt
-
Editorial |
A decade for psychiatric disorders
There are many ways in which the understanding and treatment of conditions such as schizophrenia are ripe for a revolution.
-
News & Views |
 Editing out fear
Editing out fear
Retrieving a memory initiates a window of vulnerability for that memory. Simple behavioural methods can modify distressing memories during this window, eliminating fear reactions to traumatic reminders.
- Gregory J. Quirk
- & Mohammed R. Milad
-
Opinion |
 2020 visions
2020 visions
For the first issue of the new decade, Nature asked a selection of leading researchers and policy-makers where their fields will be ten years from now. We invited them to identify the key questions their disciplines face, the major roadblocks and the pressing next steps.

 Healthy prions protect nerves
Healthy prions protect nerves The bootleggers' legacy
The bootleggers' legacy