News & Views |
Featured
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Joint effort bends membrane
Joint effort bends membrane
The curvature of cellular membranes is generated by proteins and lipids. A synthetic experimental system allows the interplay between protein- and lipid-generated bending mechanisms to be studied directly.
- Michael M. Kozlov
-
News & Views |
 Barefoot running strikes back
Barefoot running strikes back
Detailed analyses of foot kinematics and kinetics in barefoot and shod runners offer a refined understanding of bipedalism in human evolution. This research will also prompt fresh studies of running injuries.
- William L. Jungers
-
News Feature |
 Literature mining: Speed reading
Literature mining: Speed reading
Scientists are struggling to make sense of the expanding scientific literature. Corie Lok asks whether computational tools can do the hard work for them.
- Corie Lok
-
News Feature |
 Translational research: Talking up translation
Translational research: Talking up translation
Alan Ashworth took a cancer drug from Petri dish to patients in near record speed. Daniel Cressey meets a biologist who is evangelical about translational research.
- Daniel Cressey
-
News |
 Fossil feathers reveal dinosaurs' true colours
Fossil feathers reveal dinosaurs' true colours
Pigment-storage sacs found in fossils give hints about hue.
- Matt Kaplan
-
Letter |
 The cells and peripheral representation of sodium taste in mice
The cells and peripheral representation of sodium taste in mice
Mammals are repelled by large concentrations of salts but attracted to low concentrations of sodium. In mice, the latter behaviour can be blocked by the ion channel inhibitor amiloride. Here, mice have been produced lacking the drug's target sodium channel, ENaC, specifically in taste receptor neurons. It is confirmed that sodium sensing, like the four other taste modalities (sweet, sour, bitter and umami), is mediated by a dedicated 'labelled line'.
- Jayaram Chandrashekar
- , Christina Kuhn
- & Charles S. Zuker
-
-
-
-
Letter |
 Hsp70 stabilizes lysosomes and reverts Niemann–Pick disease-associated lysosomal pathology
Hsp70 stabilizes lysosomes and reverts Niemann–Pick disease-associated lysosomal pathology
Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) is a molecular chaperone which, by inhibiting lysosomal membrane permeabilization, promotes the survival of stressed cells. Hsp70 is now shown to stabilize lysosomes by binding to an anionic phospholipid, BMP, resulting in stimulation of acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) activity. Notably, the decreased ASM activity and lysosomal stability seen in patients with Niemann–Pick disease can be corrected by treatment with recombinant Hsp70.
- Thomas Kirkegaard
- , Anke G. Roth
- & Marja Jäättelä
-
Review Article |
 Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing
Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing
- Timothy W. Nilsen
- & Brenton R. Graveley
-
Article |
 Systemic signals regulate ageing and rejuvenation of blood stem cell niches
Systemic signals regulate ageing and rejuvenation of blood stem cell niches
Age-associated changes in stem cell supportive niche cells are shown to deregulate normal haematopoiesis by causing haematopoietic stem cell dysfunction. Age-dependent defects in niche cells are systemically regulated and can be reversed by exposure to a young circulation or by neutralization of the conserved longevity regulator, insulin-like growth factor-1, in the marrow microenvironment.
- Shane R. Mayack
- , Jennifer L. Shadrach
- & Amy J. Wagers
-
Article |
 Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors
Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors
Mouse and human fibroblasts can be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state with a combination of four transcription factors. Here, mature differentiated cells are directed, via a combination of a few transcription factors (distinct from those described for generating iPS cells), to form functional neurons in vitro, without having to revert the fibroblasts to an embryonic state.
- Thomas Vierbuchen
- , Austin Ostermeier
- & Marius Wernig
-
Letter |
 Fossilized melanosomes and the colour of Cretaceous dinosaurs and birds
Fossilized melanosomes and the colour of Cretaceous dinosaurs and birds
Here the presence of melanosomes — characteristic bodies that give feathers their colour — is demonstrated in feathers and feather-like structures of fossil early birds and dinosaurs from the Early Cretaceous Jehol Group of China. Not only is it shown that the feather–like structures of dinosaurs such as Sinosauropteryx really are akin to feathers, it is also possible to speculate in an informed way about their colour.
- Fucheng Zhang
- , Stuart L. Kearns
- & Xiaolin Wang
-
Letter |
 Microbial production of fatty-acid-derived fuels and chemicals from plant biomass
Microbial production of fatty-acid-derived fuels and chemicals from plant biomass
The increasing cost of energy and concerns about the environment have emphasized the need to find new sources of fuel, with the microbial production of high-energy fuels a promising approach. Here, Escherichia coli is engineered to produce more complex biofuels — fatty esters (biodiesel), fatty alcohols and waxes — directly from simple sugars. Some cells are further engineered to express hemicellulases, a step towards producing these compounds directly from hemicellulose.
- Eric J. Steen
- , Yisheng Kang
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
-
Article |
 Structure of a bacterial homologue of vitamin K epoxide reductase
Structure of a bacterial homologue of vitamin K epoxide reductase
The γ-carboxylation of many blood coagulation factors relies on the generation of vitamin K hydroquinone by the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR), of which the anticoagulant warfarin is an inhibitor. Here, the X-ray crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of VKOR is presented; the results have implications for the mechanism of action of mammalian VKOR and explain how mutations can cause warfarin resistance.
- Weikai Li
- , Sol Schulman
- & Tom A. Rapoport
-
Letter |
 Foot strike patterns and collision forces in habitually barefoot versus shod runners
Foot strike patterns and collision forces in habitually barefoot versus shod runners
Although humans have engaged in long-distance running either barefoot or with minimal footwear for most of human evolutionary history, the modern running shoe was not invented until the 1970s. Here, runners who habitually run in sports shoes are shown to run differently to those who habitually run barefoot, with the latter often landing on the fore-foot rather than the rear-foot. This strike pattern may have evolved to protect from some of the impact-related injuries now experienced by runners.
- Daniel E. Lieberman
- , Madhusudhan Venkadesan
- & Yannis Pitsiladis
-
News |
 Head of German drug agency to leave post
Head of German drug agency to leave post
Board calls time on embattled director of pharmaceutical evaluation institute.
- Quirin Schiermeier
-
News |
 Men prefer less powerful women
Men prefer less powerful women
The positioning of people's photos affects how attractive and powerful they seem to be.
- Matt Kaplan
-
News |
 Stem-cell line given the nod
Stem-cell line given the nod
NIH moves to approve cells in limbo after rule change.
- Brendan Borrell
-
News |
 Hiding place for missing heritability uncovered
Hiding place for missing heritability uncovered
Rare mutations linked to disease may hide in common variants.
- Brendan Maher
-
News |
 Healthy prions protect nerves
Healthy prions protect nerves
The proteins that can cause CJD have a vital role in the nervous system.
- Alison Abbott
-
Letter |
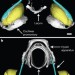 A bony connection signals laryngeal echolocation in bats
A bony connection signals laryngeal echolocation in bats
Echolocation is usually associated with bats. Many echolocating bats produce signals in the larynx, but a few species produce tongue clicks. Here, studies show that in all bats that use larynx-generated clicks, the stylohyal bone is connected to the tympanic bone. Study of the stylohyal and tympanic bones of a primitive fossil bat indicates that this species may have been able to echolocate, despite previous evidence to the contrary, raising the question of when and how echolocation evolved in bats.
- Nina Veselka
- , David D. McErlain
- & M. Brock Fenton
-
Letter |
 Animal cryptochromes mediate magnetoreception by an unconventional photochemical mechanism
Animal cryptochromes mediate magnetoreception by an unconventional photochemical mechanism
Animals use the Earth's magnetic field for orientation but the biophysical basis of this is unclear. The light-dependent magnetic sense of Drosophila melanogaster was recently shown to be mediated by the cryptochrome (Cry) photoreceptor; here, using a transgenic approach, the type 1 and 2 Cry of the monarch butterfly are shown to both function in the magnetoreception system of Drosophila, and probably use an unconventional photochemical mechanism.
- Robert J. Gegear
- , Lauren E. Foley
- & Steven M. Reppert
-
News |
 Europe cannot keep its promises on fish stocks
Europe cannot keep its promises on fish stocks
Even with total cessation of fishing, UN target would still be missed.
- Daniel Cressey
-
Letter |
 Genome-wide erasure of DNA methylation in mouse primordial germ cells is affected by AID deficiency
Genome-wide erasure of DNA methylation in mouse primordial germ cells is affected by AID deficiency
The extent of epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian primordial germ cells (PGCs) and in early embryos, and its molecular mechanisms, are poorly understood. DNA methylation profiling in PGCs now reveals a genome–wide erasure of methylation, with female PGCs being less methylated than male ones. A deficiency of the cytidine deaminase AID interferes with the genome–wide erasure of DNA methylation, indicating that AID has a critical function in epigenetic reprogramming.
- Christian Popp
- , Wendy Dean
- & Wolf Reik
-
News |
 Virus spreads by bouncing off infected cells
Virus spreads by bouncing off infected cells
Viral ping-pong lets vaccinia get to other cells faster.
- Brian Vastag
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Brinster et al. reply
Brinster et al. reply
- Sophie Brinster
- , Gilles Lamberet
- & Claire Poyart
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional role of cyclin D1 in development revealed by a genetic–proteomic screen
Transcriptional role of cyclin D1 in development revealed by a genetic–proteomic screen
Although cyclin D1 is frequently overexpressed in human cancers, the full range of its functions in normal development and oncogenesis is unclear. Here, tagged cyclin D1 knock-in mouse strains are developed to allow a search for cyclin D1-binding proteins in different mouse organs using high-throughput mass spectrometry. The results show that, in addition to its established cell cycle roles, cyclin D1 has an in vivo transcriptional function in mouse development.
- Frédéric Bienvenu
- , Siwanon Jirawatnotai
- & Piotr Sicinski
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Essentiality of FASII pathway for Staphylococcus aureus
Essentiality of FASII pathway for Staphylococcus aureus
- Wendy Balemans
- , Nacer Lounis
- & Anil Koul
-
News |
 Superbug family tree sketched out
Superbug family tree sketched out
Next-generation genome sequencing enables detailed tracking of MRSA infections.
- Lucas Laursen
-
Article |
 A synchronized quorum of genetic clocks
A synchronized quorum of genetic clocks
A defining focus of synthetic biology is the engineering of genetic circuits with predictive functionality in living cells. Here, a decade after the first synthesized genetic toggle switch and oscillator, an engineered gene network with global intercellular coupling is designed that is capable of generating synchronized oscillations in a growing population of cells.
- Tal Danino
- , Octavio Mondragón-Palomino
- & Jeff Hasty
-
Letter |
 FOXO-dependent regulation of innate immune homeostasis
FOXO-dependent regulation of innate immune homeostasis
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are an important class of immune effector molecules which fight pathogen infections. AMP induction in Drosophila is regulated through the activation of the Toll and immune deficiency pathways; it is now shown that AMP activation can be achieved independently of these pathways by the transcription factor FOXO. In non-infected animals, AMP genes are activated in response to nuclear FOXO activity when induced by starvation.
- Thomas Becker
- , Gerrit Loch
- & Michael Hoch
-
Letter |
 Mutational robustness can facilitate adaptation
Mutational robustness can facilitate adaptation
If robustness is the opposite of evolvability, we might expect that a robust population would have difficulty adapting to environmental change; however, some studies have suggested that genetic robustness facilitates adaptation. Here, using a general population genetics model, mutational robustness is found to either impede or facilitate adaptation depending on the population size, the mutation rate and the structure of the fitness landscape.
- Jeremy A. Draghi
- , Todd L. Parsons
- & Joshua B. Plotkin
-
Letter |
 Mechanism of folding chamber closure in a group II chaperonin
Mechanism of folding chamber closure in a group II chaperonin
Group II chaperonins are present in eukaryotes and archaea and are essential mediators of cellular protein folding. This process is critically dependent on the closure of a built-in lid, which is triggered by ATP hydrolysis, but the structural rearrangements and molecular events leading to lid closure are unknown. Using cryo-electron microscopy, the structures of an archaeal group II chaperonin in the open and closed states are now reported, providing details of this mechanism.
- Junjie Zhang
- , Matthew L. Baker
- & Wah Chiu
-
Research Highlights |
Neuropharmacology: Beating depression
-
-
Research Highlights |
Biochemistry: Designer label
-
Research Highlights |
Evolutionary biology: How girls go solo
-
Research Highlights |
Ecology: Asocial invaders
-
Research Highlights |
 Evolutionary biology: Sperm signals
Evolutionary biology: Sperm signals
-
Editorial |
Ten years of synergy
Contributions to and from basic science are the part of synthetic biology that most deserves celebration.
-
Correspondence |
Conservation work is incomplete without cryptic biodiversity
- Genoveva F. Esteban
- & Bland J. Finlay
-
Research Highlights |
 Microbiology: Life in the lost city
Microbiology: Life in the lost city
-
News & Views |
 How cilia beat
How cilia beat
Physics provides new approaches to difficult biological problems: a plausible mathematical model of how cilia and flagella beat has been formulated, but it needs to be subjected to rigorous experimental tests.
- T. J. Mitchison
- & H. M. Mitchison
-
News & Views |
 Decoding a national treasure
Decoding a national treasure
The giant-panda genome is the first reported de novo assembly of a large mammalian genome achieved using next-generation sequencing methods. The feat reflects a trend towards ever-decreasing genome-sequencing costs.
- Kim C. Worley
- & Richard A. Gibbs
-
News & Views |
 Synchronized bacterial clocks
Synchronized bacterial clocks
By synchronizing clocks, humans make more efficient use of their time and orchestrate their activities in different places. Bacteria have now been engineered that similarly coordinate their molecular timepieces.
- Martin Fussenegger
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemistry
- Biological techniques
- Biophysics
- Biotechnology
- Cancer
- Cell biology
- Chemical biology
- Computational biology and bioinformatics
- Developmental biology
- Drug discovery
- Ecology
- Evolution
- Genetics
- Immunology
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Neuroscience
- Physiology
- Plant sciences
- Psychology
- Stem cells
- Structural biology
- Systems biology
- Zoology

 Stability in times of stress
Stability in times of stress Deciphering the printed word
Deciphering the printed word The endocytic matrix
The endocytic matrix Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton
Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton Chromatin remodelling during development
Chromatin remodelling during development Towards building a chromosome segregation machine
Towards building a chromosome segregation machine